Determination of Diode Characteristics:
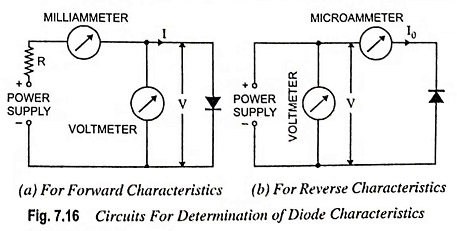
Determination of Diode Characteristics – The forward characteristics of a diode can be obtained by use of the circuit depicted in Fig. 7.16 (a). The diode voltage is set at a series of convenient levels, and the corresponding current levels are measured and recorded. The characteristics are then plotted from the values obtained.
The reverse characteristics can be obtained in the same way, except that a very sensitive microammeter is required for measuring the diode reverse current. Also, the microammeter must be connected directly in series with the diode as shown in Fig. 7.16 (b); otherwise the voltmeter current may introduce a serious error.
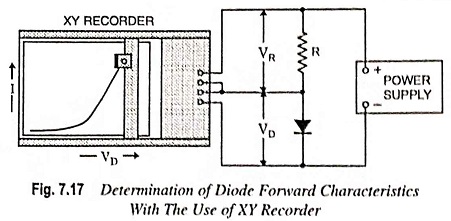
The forward characteristics of a diode can also be determined with the use of an XY recorder as shown in Fig. 7.17. The voltage across resistance R is directly proportional to the diode current I, while the voltage across the diode is of course VD. The voltage across the resistor R i.e., VR is applied to the vertical input terminals of the X-Y recorder, and voltage across the diode, VD is applied to the horizontal terminals.
When the power supply voltage is slowly increased from zero, the diode forward characteristics is traced out by the pen. If resistance R is of 1 kΩ, there is a voltage drop of 1 V across it for every 1 mA of diode current. Thus, with the scale of the XY recorder set to 1 V/cm, the (vertical) current ordinate of the graph is 1 mA/cm. A convenient scale for the (horizontal) voltage ordinate is 0.1 V/cm.