Coal Based Thermal Power Plants Articles:
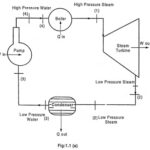
Rankine Cycle (Simple Steam Power Cycle): Rankine cycle is the theoretical cycle on which the steam turbine (engine) works. Boiler Refer the process (4) to (1): Feed water is passing to the boiler. Heat is added to the water in the boiler. The … (Read More)
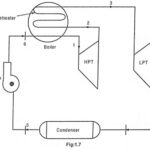
Reheat Cycle in Steam Power Plant: Reheat Cycle: If the dryness fraction of steam leaving the turbine is less than 0.88, then corrosion and erosion of turbine blades occur. To avoid this situation, reheat is used. In the reheat cycle in steam … (Read More)
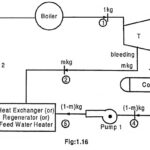
Regenerative Cycle – Definition, Advantages and Methods: Regenerative Cycle – Assume 1 kg of steam is expanded in the turbine. Before complete amount of steam is expanded, some amount of steam (m kg) is extracted (this process is called bleeding) and … (Read More)
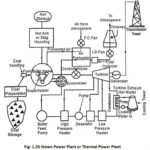
Layout of Modern Coal Power Plant or Steam Power Plant: In Coal Power Plant or Steam Power Plant, the water is converted into steam and the steam expanded in a turbine to produce kinetic energy which is converted into mechanical energy. The … (Read More)
Site Selection of Steam Power Plant: The following consideration should be taken while site selection of steam power plant. 1. Availability of raw materials Huge quantity of coal and fuel are required to run a steam (thermal) power plant. Therefore, it is important … (Read More)
Super Critical Boiler – Definition, Advantages and types: Super critical boiler is a boiler that operates at super critical pressure (high pressure) to increase the efficiency of the plant and to reduce the cost of electricity production. Normally, water tube boilers … (Read More)
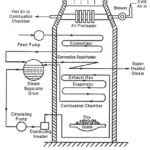
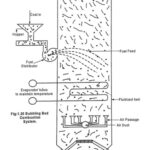
La Mont Boiler Construction and Working: This type of boiler was introduced by Lamont in 1925. The arrangement of La Mont Boiler Construction and Working is shown in the Fig. 1.30. It is a forced circulation, high pressure water tube boiler. The … (Read More)
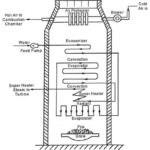
Benson Boiler – Construction, Working Principle and Advantages: In 1927, Benson boiler was developed by Benson in West Germany. It was the first super critical drumless boiler. Construction: It is a high pressure, vertical, fire tube boiler. The Fig. 1.31 shows the schematic … (Read More)
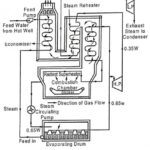
Loeffler Boiler Construction and Working Principle: The major disadvantage in La Mont boiler is the deposition of salt and sediment on the inner surface of the water tubes. It reduces the heat transfer and ultimately the generating capacity. The salt deposition … (Read More)
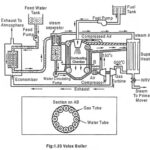
Velox Boiler – Construction, Working Principle and Advantages: Velox Boiler – When the gas velocity exceeds the sound velocity, the heat is transferred from the gas at much higher rates than rates achieved with sub-sonic flow. This advantage is used to … (Read More)
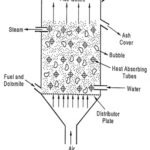
Fluidized Bed Combustion Boiler Working and Types: The coal available in India is of low quality, high ash content and low calorific value. The traditional grate fuel firing systems have got limitations and are techno-economically unviable to meet the challenges of … (Read More)
Bubbling Fluidized Bed Combustion System: In Bubbling Fluidized Bed Combustion System (or) Atmospheric bed combustion system, coal is crushed to a size of 1 – 10 mm depending upon the quality of coal and type of fuel fed into the combustion … (Read More)
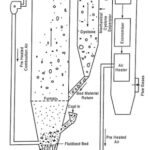
Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion System (CFBC): The Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion System (CFBC) has evolved from conventional bubbling bed combustion to over come some of the drawbacks associated with bubbling bed combustion. CFBC provides greater flexibility in burning wide range of … (Read More)
Pressurised Fluidised Bed Combustion System (PFBC): Pressurised Fluidised Bed Combustion (PFBC) system is used for large coal burning applications. The operating efficiency of PFBC is increased by introducing differential air pressure. In PFBC, coal is injected into pressurized bed of 850 – … (Read More)
Steam Turbine Working Principle and Types: Steam turbines are one of the most versatile and oldest prime movers that transform the potential energy of the steam into kinetic energy and later in turn transformed into mechanical energy – rotation of turbine … (Read More)
Steam Condenser – Definition, Working Principle and Types: Steam condenser is a device in which the exhaust steam of a turbine is condensed by means of cooling water below atmospheric pressure. By decreasing the exhaust pressure of steam below atmosphere, the … (Read More)
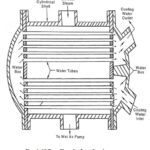
Subsystems of Thermal Power Plant: The Subsystems of Thermal Power Plant are the auxiliary plants required for the plant for its proper operation and for the increase of their efficiency. Some of the sub systems are as follows: Boiler Accessories: The appliances used to … (Read More)
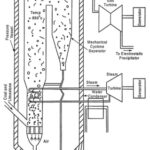
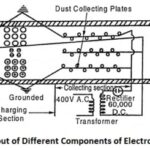
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) – Construction and Working Principle: Electrostatic Precipitator is located between the boiler and the chimney, it extracts the fly ash from the flue gases and thus prevents the fly ash from entering the atmosphere. Electrodes are used to … (Read More)
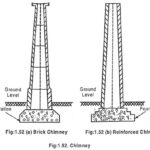
Types of Chimney in Power Plant: Chimney in Power Plant is used to release flue gas into the atmosphere. The chimney is constructed 2.5 to 3 times of height of the power plant. The main purpose of this is to emit … (Read More)
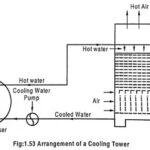
What is a Cooling Tower? – Types of Cooling Tower: Cooling Tower is used to cool the water, and its height is about 140 Meters. The hot water is to pumped the tower top and falls down through the tower and … (Read More)
What is Boiler Mountings? – Types and its Workings: The devices used for the efficient operation, proper maintenance, safe operation, etc are called Boiler mountings. The different boiler mountings are given below 1. Water Gauge or Water Level Indicator: It indicates the level … (Read More)
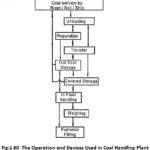
Fuel Handling System and Ash Handling System: Handling of coal: The coal handling is divided into two types: Out-plant handling. In-plant handling. 1. Out-plant handling: This handling includes the handling of coal from coal mine to the thermal power plant. These handlings are done outside the … (Read More)
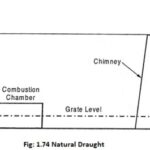
Draught System in Power Plant – Definition and Classification: Draught is an essential part in thermal power plant. The functions of the draught system are: To supply required quantity of air to the furnace for combustion of fuel. To draw the combustion products … (Read More)
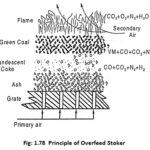
Overfeed Stoker and Underfeed Stoker – Definition and Types: There are two common methods used for burning coal. 1. Stoker firing 2. Pulverised fuel firing. The stoker firing method is used for firing solid coal where as pulverised firing method is used for … (Read More)
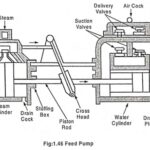
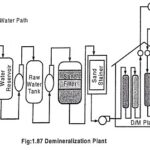
Feed Water Treatment in Power Plant and Types: Raw water coming from different sources contains dissolved salts and un-dissolved or suspended impurities. Therefore it is necessary to remove harmful salts dissolved into the water before feeding it to the boiler. It … (Read More)
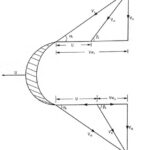
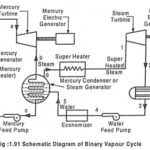
Binary Vapour Cycle – Schematic Diagram and its Workings: The maximum efficiency is achieved in carnot cycle. To increase the efficiency of the actual engine, ie to approach the carnot cycle efficiency, the total heat should be supplied at constant temperature T1 … (Read More)
Waste Heat Recovery System: Waste heat recovery system is the heat which is not at all used and exhausted out as a waste product. Waste heat is normally available from the industry in the form of process steam and water at … (Read More)