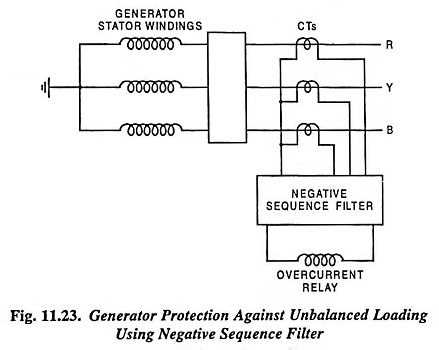
Negative Sequence Protection of Generator against Unbalanced Loads:
If, owing to a fault, there is an imbalance in the three-phase stator currents, double frequency currents are induced in the rotor core. This causes overheating of rotor and possible damage to the rotor. Unbalanced stator currents also cause severe vibrations and heating of stator. Current balance relaying equipment would not be very effective for protection against such faults because such equipment energized by phase currents would operate quickly for small imbalances and too slowly for large imbalances. Negative Sequence Protection of Generator with overcurrent relay is used to provide protection against unbalanced loading.
From the theory of symmetrical components we know that unbalance three-phase currents have a negative sequence component. The negative phase sequence current causes heating of the stator. In case of high speed turbogenerators, the continuous current which can be carried is usually in the range of 10 and 15 per cent of the positive sequence continuous rating. The negative sequence heating follows a normal resistance law and so it is proportional to the square of the current. The heating time constant of the machine largely depends upon the cooling system used and is expressed as I22 t = K where I2 is the negative sequence current expressed on the per unit basis of the continuous maximum rating, t is the current duration in seconds, and K is a constant which for turbogenerators usually lies between 3 and 20.
It is generally necessary to install negative sequence relays that match the above heating characteristic of the machine. The arrangement of Negative Sequence Protection of Generator against Unbalanced Loading is shown in Fig. 11.23. Three CTs are connected in the three phases and the output from their secondaries is fed to the coil of the overcurrent relay through a negative phase sequence filter. Negative sequence filter circuit comprises resistors and inductors connected in such a way that negative sequence component flows through the relay coil. The overcurrent relay used is with inverse characteristics matching with I22 t rating curve of the machine. The relay can be set to operate at a particular value of the imbalanced current or the negative sequence component current.