Amplifier Frequency Response Articles:
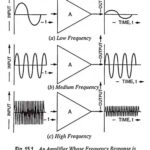
What is Frequency Response of an Amplifier?: The voltage gain of an amplifier varies with signal frequency due to the effect of variations in circuit capacitive reactance with signal frequency on the output voltage. The curve drawn between the voltage gain … (Read More)
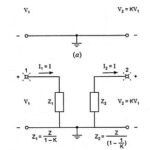
Millers Theorem and its Equivalent Circuit: Millers theorem – Consider an arbitrary circuit shown in Fig. 15.13(a). As part of a larger network that is not shown, we have isolated two circuit nodes, labelled 1 and 2, between which an impedance … (Read More)
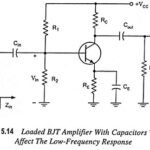
Low Frequency Response of BJT Amplifier: For analysis, we will consider the loaded voltage-divider BJT bias configuration. But the results can be applied to any configuration. For the network shown in Fig. 15.14 the capacitors Cin, Cout and CE will determine the … (Read More)
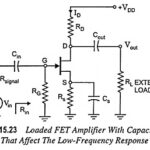
Low Frequency Response of FET Amplifier: The analysis of the Low Frequency Response of FET Amplifier is quite similar to that of the BJT amplifier. Though here common-source configuration is considered but the results can be applied to most FET configurations. … (Read More)
Effect of Internal Transistor Capacitance: As we know already that at high frequencies, the coupling and bypass capacitors act as short circuit due to their low reactance and hence the voltage gain is not affected. However, the internal Transistor capacitance play … (Read More)
Miller Effect in Amplifier Frequency Response: According to this effect, when viewed from the input base terminal of the CE-connected transistor the capacitance Ccb appears as (1 – Av)Ccb i.e., it is amplified by a factor of (1 – Av). In fact Miller … (Read More)