What is Analog Signal and Digital Signal?
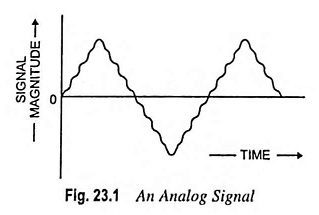
What is Analog Signal and Digital Signal? – In communication systems, a signal means a time varying electrical signal which contains all information or intelligence. The analog signal is that type of signal which varies smoothly and continuously with time. This means that analog signals are defined for every value of time and they take on continuous values in a given time interval. Thus, we can say that analog messages are characterized by data whose values vary over a continuous range. The signal depicted in Fig. 23.1 is an analog signal.
For an analog signal, the name derives from the fact that such a signal is analogous to the physical signal that it represents. The vast majority of signals in the world around us are analog. For example, the temperature or the atmospheric pressure of a certain location may vary over a continuous range and may assume an infinite number of possible values. Similarly, a speech waveform is an analog signal since it has amplitudes that vary over a continuous range.
The analog signals can be easily generated. For instance, pressure variations in air produced by sound waves can be converted into corresponding current or voltage variations with the help of microphone. Similarly, a photodiode can be used to convert light intensity variations into corresponding current or voltage variations.
An alternative form of signal representation is that of a sequence of numbers, each number representing the signal magnitude at an instant of time. The resulting signal is called a digital signal. Digital messages are constructed with a finite number of symbols. For example, the printed language consists of 26 letters, 10 digits, a space and several punctuation marks. Thus, any text is a digital message constructed from about 50 symbols.
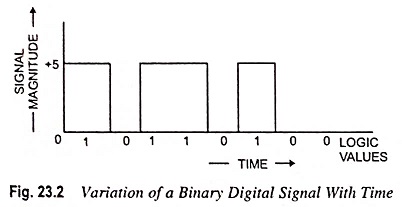
Now, since a digital signal is represented only by digits, therefore, any number system (binary, decimal, octal or hexadecimal) can be used for representation of a digital signal. However, in practice, binary number system is used to represent a digital signal. In a binary number system, each digit in the number takes on one of only two possible values, denoted 0 and 1. Correspondingly, the digital signals in binary systems need have only two voltage levels which may be labelled low and high. Figure 23.2 shows a digital signal. The waveform depicted in Fig. 23.2 is a pulse train with 0 V representing a ‘0’ signal or logic ‘0’ and +5 V representing logic ‘1’.