Apparatus Protection in Power System Articles:
Transformer Protection Types: Nature of Transformer Faults: Power transformers, being static, totally enclosed and oil immersed develop faults only rarely but the consequences of even a rare fault may be serious, unless the transformer is quickly disconnected from the system. For … (Read More)
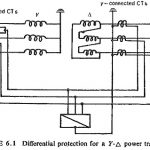
Differential Protection of Transformers: Differential Protection of Transformers is the most important type of protection used for internal phase-to-phase and phase-to-earth faults and is generally applied to transformers having ratings of 5 MVA and above. The principle of a differential relay … (Read More)
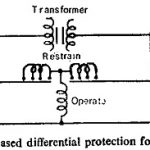
Percentage Biased Differential Relay: In order to avoid undesirable operation on heavy external faults due to CT errors and ratio change as a result of tap changing, a restraining winding is provided which is energized by … (Read More)
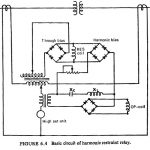
Inrush Currents in Transformer: Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformer contain pronounced harmonics but the current during internal fault conditions is sinusoidal. Advantage is taken of this fact in the design of the relay. It was pointed out earlier that for high … (Read More)
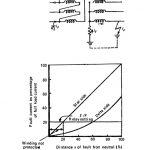
Star Winding and Delta Winding: The magnitude of earth-fault current for a given fault position within a winding depends upon the winding connections and the method of neutral earthing. The two conditions for earth-fault current … (Read More)
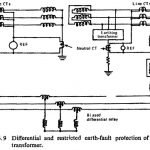
Restricted Earth Fault Protection: This type of Restricted Earth Fault Protection is provided to detect earth-faults within the protected zone of the transformer. A CT is fitted in each connection to the protected winding, and the CT secondary windings are connected … (Read More)
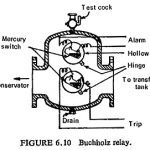
Gas Actuated Relays: When a fault occurs inside the transformer tank gas is usually generated, slowly for an incipient fault and violently for heavy faults. Most short circuits developed either by impulse breakdown between adjacent turns at … (Read More)
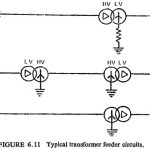
Transformer Feeder Protection: In order to supply bulk power from a major switching station, the transformer is sometimes connected directly to the feeder without an HV switchgear at the transformer. Although such a scheme provides considerable saving … (Read More)
Generator Faults: Generator faults can be considered under the following heads. (a) Stator Faults: These include the following: Phase-to-earth faults. Phase-to-phase faults. Inter-turn faults. Most faults occur in the stator windings and their connections and majority of these are earth faults. Phase faults and inter-turn faults an … (Read More)
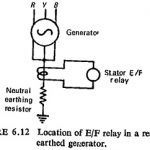
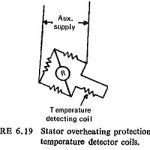
Stator Protection: The type of stator faults likely to occur have been discussed already. The earth-fault current is usually limited by resistance in the neutral of the generator. Depending upon the amount of resistance in the neutral circuit … (Read More)
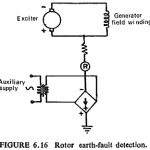
Rotor Protection: As pointed earlier rotor windings may be damaged by earth faults or open circuits. Figure (6.16) shows a modern method of rotor earth-fault detection. The field is biased by a d.c. voltage which causes current to … (Read More)
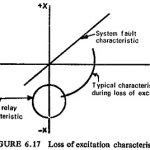
Loss of Excitation Protection: Two distinct effects of Loss of Excitation Protection are that the machine starts drawing magnetizing current of large magnitude from the system, and the slip frequency emfs induced in the rotor circuit; both of them cause overheating … (Read More)
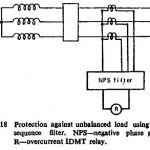
Unbalanced Loading Protection of Generator: Whatever be the cause of the unbalance it is obvious that the negative phase sequence current will result in heating of the stator. In case of high-speed turbo-generators, the continuous … (Read More)
Overload Protection Relay: Continuous balanced overloading of a machine causes overheating in the stator winding. An obvious solution to this is the application of overcurrent relays; but this is not usually provided because this discriminates by time, … (Read More)
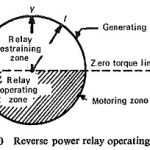
Prime Mover Protection: In the event of prime-mover failure the machine starts motoring meaning thereby that it draws electrical power from the system and drives the prime-mover. This condition imposes a balanced load on the system, which can be detected by … (Read More)
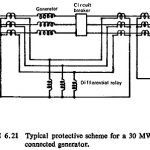
Direct Connected Generator Protection: Direct connected generators are normally of smaller ratings and a typical scheme of Direct Connected Generator Protection for a 30 MW generator is shown in Fig. (6.21). It consists of the following protections: Unbiased differential protection. Backup overcurrent protection. Negative phase … (Read More)
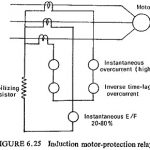
Motor Protection: There is a wide range of motors in existence for various purposes. However, the fundamental problems affecting the choice of protection are independent of the type of motor and the type of load to which it … (Read More)
Bus Zone Protection: Bus Zone Protection includes, besides the bus itself the apparatus such as circuit breakers, disconnecting switches, instrument transformers and bus sectionalizing reactors, etc. Although bus zone faults are rare, experience shows that bus zone protection is highly desirable … (Read More)