Application of Relay Articles:
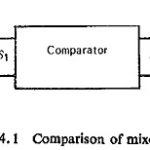
Comparator Equation in Power System Protection: Taking a very general case to cover the complete range of conventional relay characteristics, let S1 and S2 be the two input signals such that when the phase relationship … (Read More)
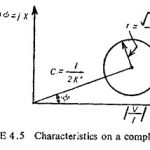
General Equation for Electromagnetic Relay: It has already been shown that when not more than two quantities are involved, the equation for the characteristic of the relay at the threshold of operation under steady state conditions, when plotted on complex planes … (Read More)
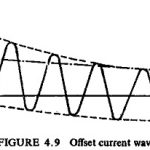
Overcurrent Relay Characteristics: The operating time of all Overcurrent Relay Characteristics tends to become asymptotic to a definite minimum value with increase in the value of current. This is inherent in electromagnetic relays due to saturation of the magnetic circuit. So … (Read More)
Instantaneous Overcurrent Relays: If the relay operates instantly without any intentional time delay, this characteristic can generally be satisfied by a relay of the non-polarized attracted armature type. This relay has a special advantage of reducing the time of operation to … (Read More)
Time Current Relay Application: Overcurrent and earth fault protective gear can be made discriminative by grading the operating times of successive devices. The pickup currents are adjusted in such a way that the protection nearest the … (Read More)
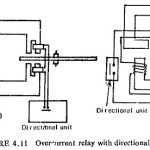
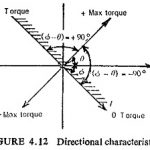
Directional Relays: Selective protection cannot be achieved with time graded overcurrent protection systems in ring or loop systems as well as in radial circuits with two end power supply. A directional feature is incorporated in the Directional Relays as shown in … (Read More)
Single Phase Directional Relay: The general Eq. (4.8) suggests that for directional control the individual torques, viz. K |A|2 and K′ |B|2 should be eliminated. Considering a voltage current directional relay the general Eq. (4.8) reduces to The spring constant … (Read More)
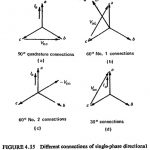
Directional Overcurrent Relays in Power Systems: Relay connections must be made so that the currents and voltages applied to the relay during the various fault conditions which may arise on the protected circuit section … (Read More)
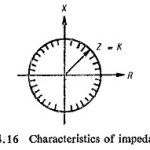
Distance Relays Types and their Applications: In applying relays to a transmission system it is necessary to state the relay characteristic in the same terms that the system conditions are stated. This is especially true of Distance Relays Types. If the … (Read More)
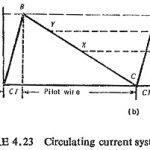
Differential Relay Application: The principle of operation depends on a simple circulating current principle where the difference of the currents of the two CTs flows through the relay under normal conditions or even under faults outside the protected section. This is … (Read More)