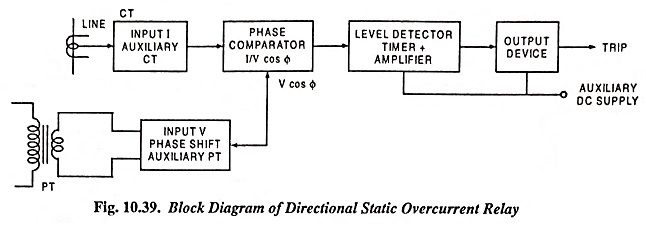
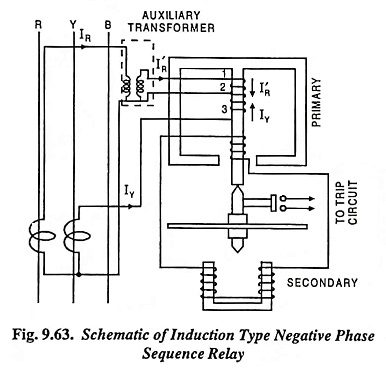
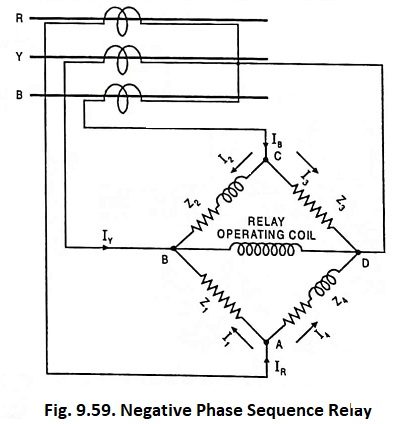
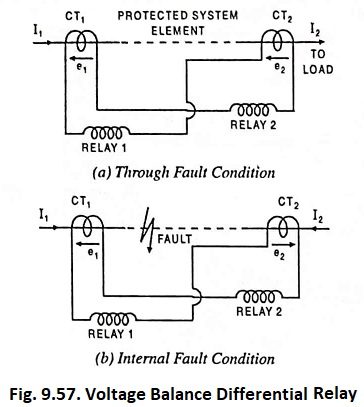
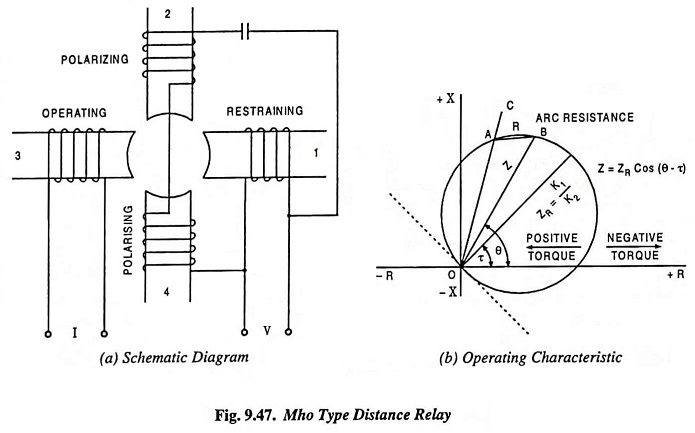
Directional Static Overcurrent Relay
Directional Static Overcurrent Relay: For obvious reasons of obtaining selectivity overcurrent relays are made directional. Directional static overcurrent relay senses direction of power flow by means of phase angle between V and I. When the…