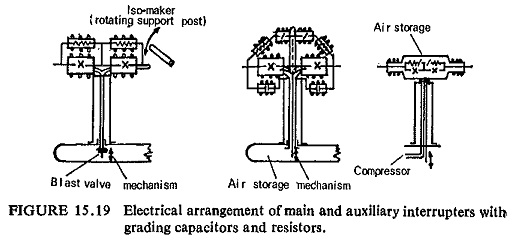
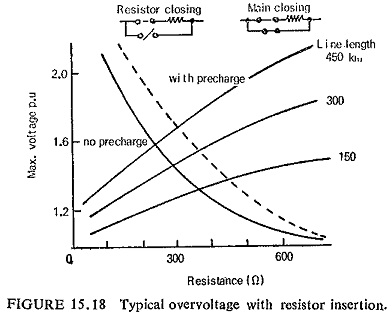
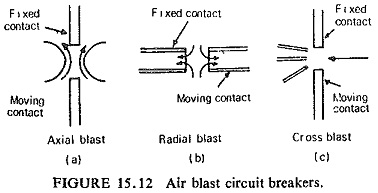
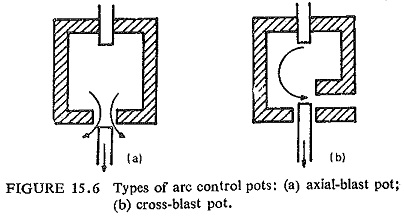
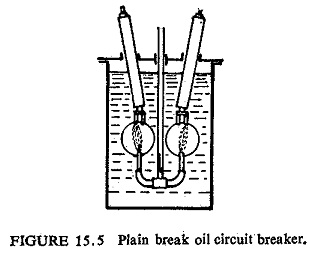
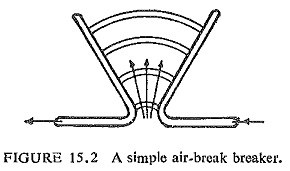
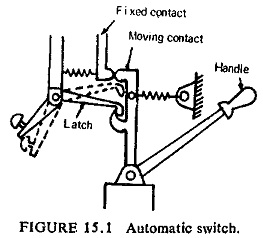
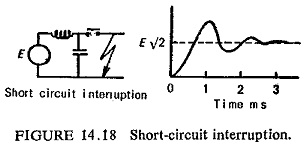
Development of Airblast Circuit Breaker
Development of Airblast Circuit Breaker: The development of Airblast circuit breakers has taken place in three stages shown schematically in Fig. (15.19): Momentarily pressurized Airblast breakers with isomaker in the Momentarily pressurized air-blast breakers with…