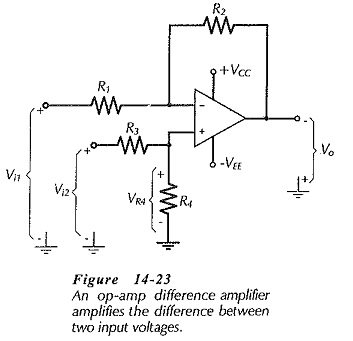
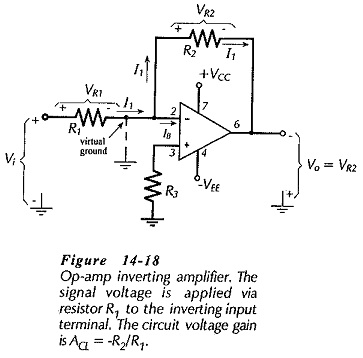
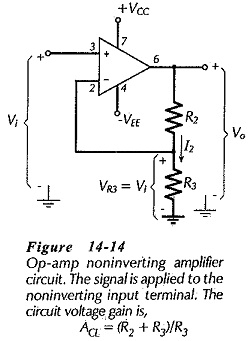
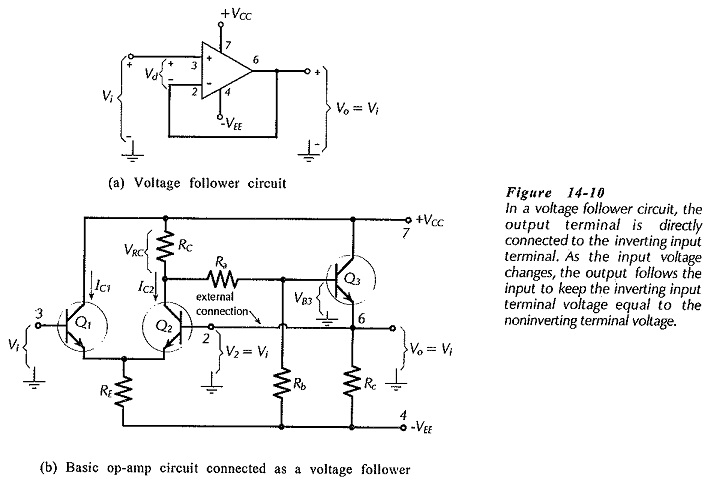
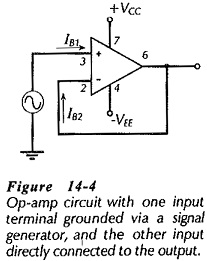
Operational Amplifier Circuit Stability
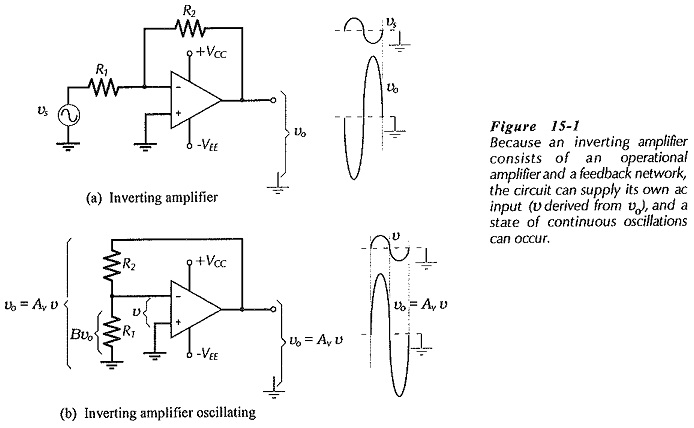
Operational Amplifier Circuit Stability: Loop Gain and Loop Phase Shift - Consider the inverting amplifier circuit and waveforms in Fig. 15-1(a). The signal voltage voltage (vs) is amplified by a factor R2/R1, and phase shifted…