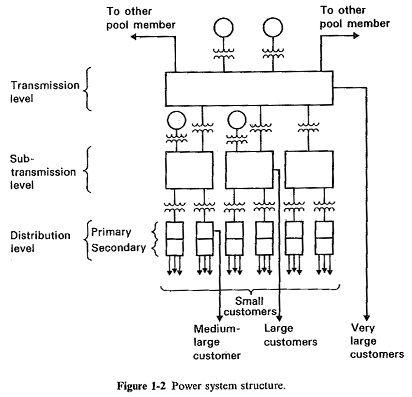
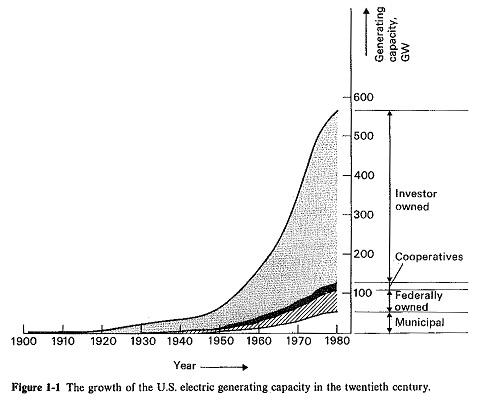
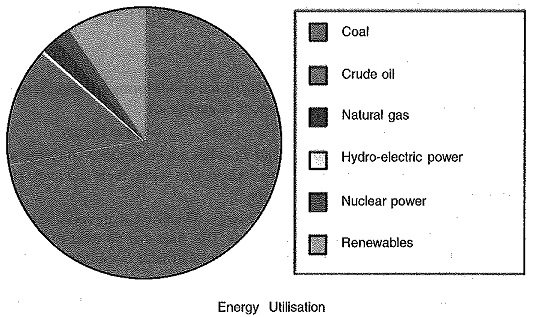
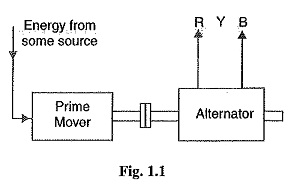
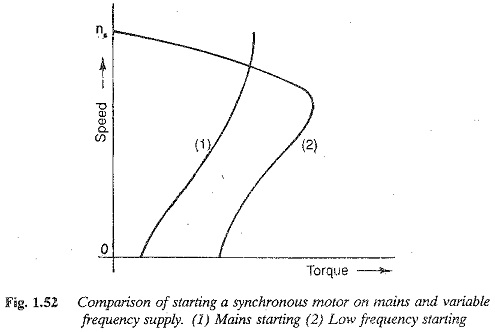
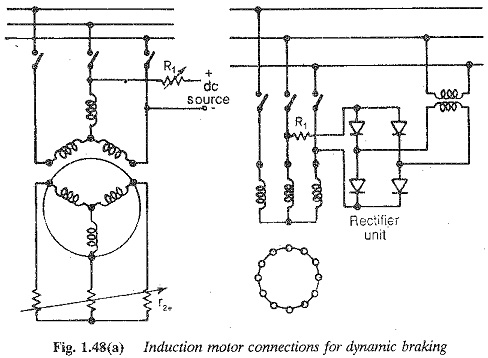
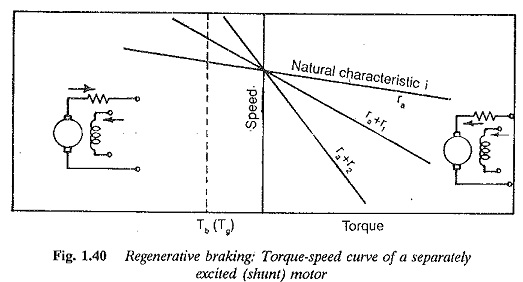
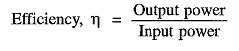Structure of Power System of Energy Electric System
Structure of Power System of Energy Electric System: An Structure of Power System, even the smallest one, constitutes an electric network of vast complexity. The one factor that determines the system structure more than any…