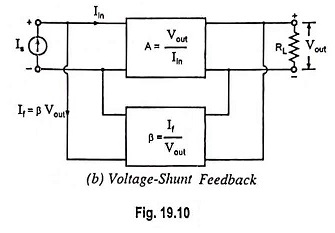
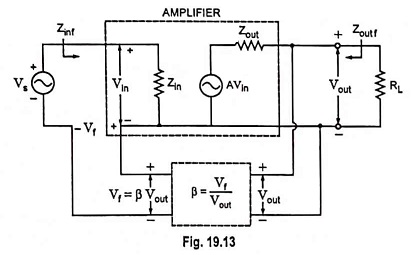
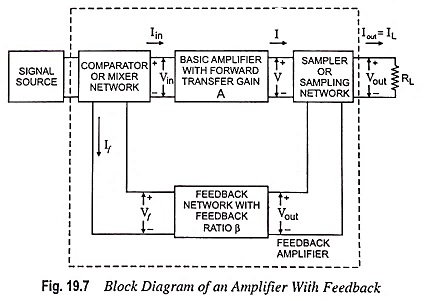
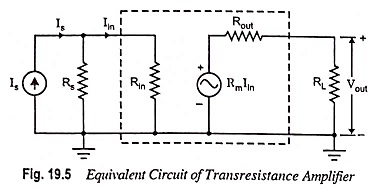
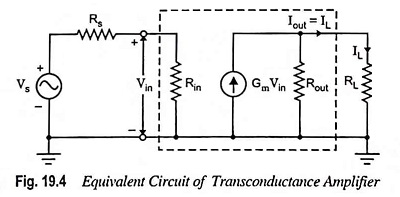
Voltage Shunt Feedback Amplifier Circuit
Voltage Shunt Feedback Amplifier Circuit: Voltage Shunt Feedback Amplifier Circuit is also known as shunt-derived shunt fed feedback or voltage shunt inverse feedback. Here, a small portion of the output voltage is coupled back to…