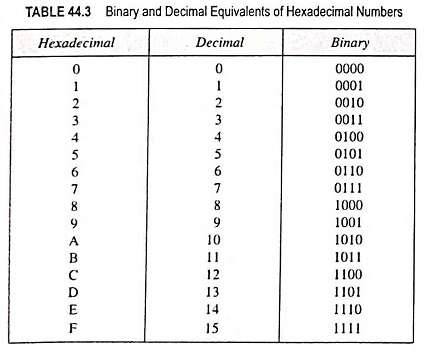
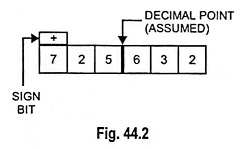
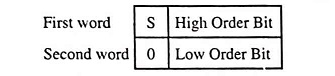
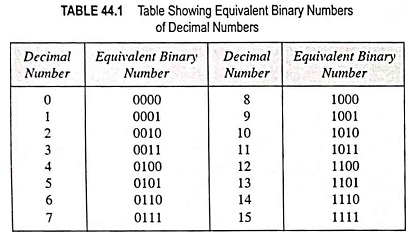
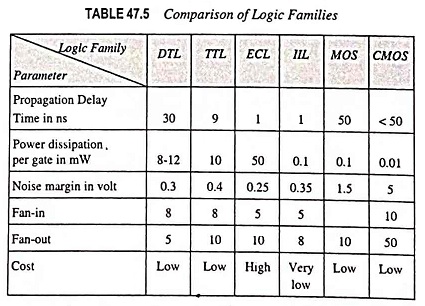
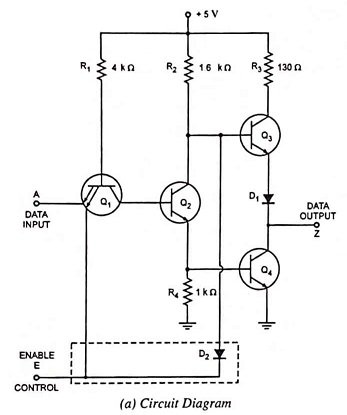
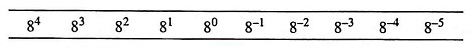Hexadecimal Number System (Definition, Conversions & Examples)
Hexadecimal Number System (Definition, Conversions & Examples): The binary number system forms the natural choice for the two-state systems. But in this system, the numbers tend to get short rather long. Hence to reduce the…