Basic Components of Static Relays Articles
Semiconductor Diodes in Static Relays: The pn junction has rectifying characteristics as shown in Fig. (10.1). If a source of emf is connected to the pn junction in the polarity shown in Fig. (10.1a), then … (Read More)
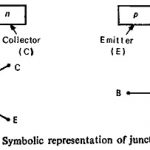
Transistor Use in Static Relay: In its simplest form, it consists of two pn junction diodes coupled together by a very thin common base, either of p-type or n-type semiconductor material. It is possible to … (Read More)
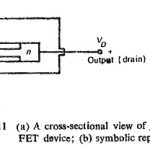
Field Effect Transistor in Static Relay: Field Effect Transistor in Static Relay is a unipolar device as compared to bipolar transistor already discussed. It consists of a bar of semiconductor material whose resistance is modulated by varying either the cross-sectional area … (Read More)
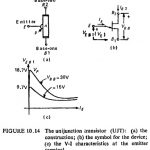
Unijunction Transistor in Static Relay: Unijunction Transistor in Static Relay is a three terminal device with only one pn-junction. It is made up of n-type silicon wafer having two base controls and a p-type alloy junction which acts as emitter electrode. In … (Read More)
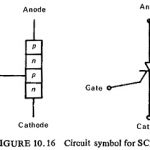
Thyristor in Static Relay: The structure of Thyristor in Static Relay consists of four alternate p-and n-type layers. In the thyristor (also called a silicon controlled rectifier—SCR) connections are made available to the inner layers. It acts like two transistors in … (Read More)
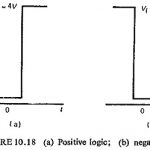
Logic Circuit in Static Relay: The concept of Logic Circuit in Static Relay can be better understood by considering the logic operations performed by the devices rather than the actual happenings that occur during their operation. This makes complex static relay … (Read More)
Smoothing Circuits: The rectified a.c. consists of a series of undirectional half waves of current or voltage. It is generally desirable to smooth this output. The various filters used for Smoothing Circuits are the conventional RC filter, RC chain filter, transistorized … (Read More)
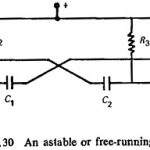
Square Wave Generators: Diode clippers can be used to remove the curved portion of the sinusoidal wave to give square waves. The operational amplifier together with an integrator, can be used to generate a square wave. The simplest form of the … (Read More)
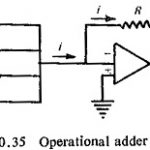
Summation Device: Summation transformers and sequence networks as already discussed can combine a number of electrical quantities into a single quantity. The operational amplifier is commonly used as a mixer or summer and the Summation Device is shown in Fig. (10.35). … (Read More)
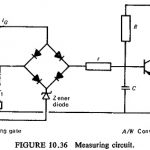
Sampling Circuits: Sampling Circuits is one which allows a comparison of instantaneous values derived at different instants of time, thereby dispensing with the need to phase shift and mix signals derived from the primary line quantities. Figure (10.36) shows a sampling circuits … (Read More)
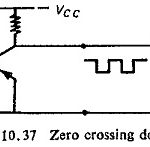
Zero Crossing Detector Circuit: Zero Crossing Detector Circuit basically involves the sine to square wave conversion by a level detector circuit followed by a pulse circuit, which consists of one shot monostable circuit or a differentiator. The zero crossing detection is … (Read More)