Basics of Electronics Engineering Articles:
Types of Power Supply in Electronics: There are two types of Power Supply in Electronics viz. dc supply and ac supply. The voltage or current available from batteries or solar cells is direct in the sense that the polarity remains the same. … (Read More)
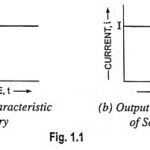
What is Voltage and Current?: There are two quantities that we like to keep track of in electronic circuits : voltage and current. These are usually changing with time; otherwise nothing interesting in happening. Voltage (abbreviated as V or sometimes E) between … (Read More)
What is Active Components and Passive Components?: All electronic circuits, however complicated, contain a few basic components (generally speaking, only five)—three passive and two active components. Though passive components by themselves are not capable of amplifying or processing an electrical signal … (Read More)
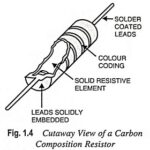
What is Resistor in Electronics?: Resistance is a dissipative element, which converts electrical energy into heat, when the current flows through it in any direction. The process of energy conversion is irreversible. The circuit element used … (Read More)
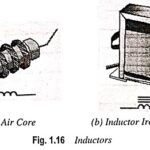
What is Inductor in Electronics?: An inductor has been defined as a physical device which is capable of storing energy by virtue of a current flowing through it. An Inductor in Electronics is a circuit component which opposes the change of … (Read More)
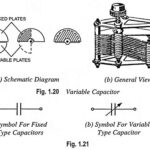
What is Capacitor in Electronics?: What is Capacitor in Electronics? – Capacitor is a two-terminal element that has the capability of charge storage and, consequently, energy storage. The stored energy can be fully retrieved. The current through the capacitor is proportional to … (Read More)
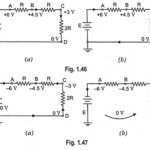
Zero Reference Level in Electronics Engineering: Zero Reference Level – In order to avoid errors in the measurement of different voltages in an electronic circuit, it is imperative to select some common point, known as reference, zero potential or datum point … (Read More)