BJT Specifications Articles:
Transistor Datasheet: To select a transistor for a particular application, the Transistor Datasheet provided by device manufacturers must be consulted. Most data sheets start off with the device type number at the top of the page, a descriptive title, and a list … (Read More)
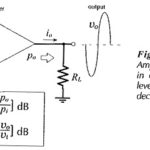
Decibels and Half Power Point Method: Power Measurement in Decibels and Half Power Point Method – The power gain (Ap) of an amplifier may be expressed in terms of the log of the ration of output power (po) to input power … (Read More)
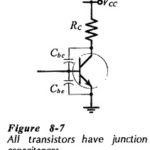
BJT Cutoff Frequency and Capacitance: Device Cutoff Frequency – All transistors have junction capacitances. The junction capacitances and the transit time of charge carriers through the semiconductor material limit the high frequency performance of the device. This limitation is expressed as … (Read More)
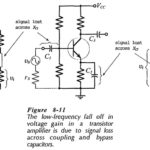
High Frequency Analysis of BJT: Coupling and Bypass Capacitor Effects – Consider the typical High Frequency Analysis of BJT illustrated in Fig. 8-5. As discussed, the amplifier voltage gain is constant over a middle range of signal frequencies, and it falls … (Read More)
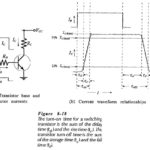
Transistor Switching Times: For Transistor Switching Times, the switching speed of the device can be an important quantity. Consider the circuit in Fig. 8-18(a). When the base input current is applied, the transistor does not switch on immediately. Like frequency response, … (Read More)
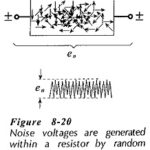
Transistor Circuit Noise: Unwanted signals at the output of an electronics system are termed noise. The noise amplitude may be large enough to severely distort, or completely swamp, the wanted signals. Consequently, the noise level dictates the minimum signal amplitude that … (Read More)
Power Dissipation Rating in Transistor: Maximum Power Dissipation – Consider the portion of the data sheet for the 2N3903 and 2N3904 transistor reproduced in Fig. 8-24. The total device dissipation (PD) is specified as 625 mW at a maximum ambient temperature (TA) … (Read More)
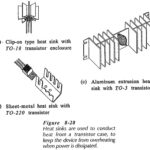
Heat Sink in Transistor: When power is dissipated in a transistor, the heat generated must flow from the collector-base junction to the case, and then to the surrounding atmosphere. When only a very small amount of power is involved, as in … (Read More)