Breakdown in Solid Dielectrics Articles:
Solid Dielectric Materials: Solid dielectric materials are used in all kinds of electrical apparatus and devices to insulate one’current carrying part from another when they operate at different voltages, A good dielectric should have low dielectric loss, high mechanical strength, should … (Read More)
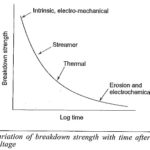
Intrinsic Breakdown: When voltages are applied only for short durations of the order of 10-8 s the dielectric strength of a solid dielectric increases very rapidly to an upper limit called the intrinsic electric strength. Experimentally, this highest dielectric strength can … (Read More)
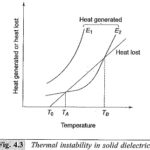
Electromechanical Breakdown and Thermal Breakdown: Electromechanical Breakdown: When solid dielectrics are subjected to high electric fields, failure occurs due to electrostatic compressive forces which can exceed the mechanical compressive strength. If the thickness of the specimen is d0 and is compressed to a … (Read More)
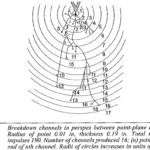
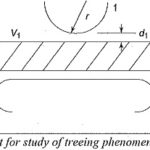
Breakdown of Solid Dielectrics in Practice: There are certain types of breakdown which do not come under either intrinsic breakdown or thermal breakdown, but actually occur after prolonged operation. These are, for example, breakdown due to tracking in which dry conducting … (Read More)
Breakdown in Composite Dielectrics: It is difficult to imagine a complete insulation system in an electrical equipment which does not consist of more than one type of insulation. If an insulation system as a whole is considered, it will be found … (Read More)
Solid Dielectrics Used in Practice: The majority of the insulating systems used in practice are solids. They can be broadly classified into three groups: organic materials, inorganic materials and synthetic polymers. Some of Solid Dielectrics Used in Practice materials are listed … (Read More)
High Temperature High Performance Polymers: High Performance Polymers films are thermoplastic and are generally transparent. The are needed for use in applications where temperatures vary from very low (- 269°C) to very high (+ 400°C) values. Such applications include space shuttle … (Read More)