Carrier Aided Distance Protection Scheme:
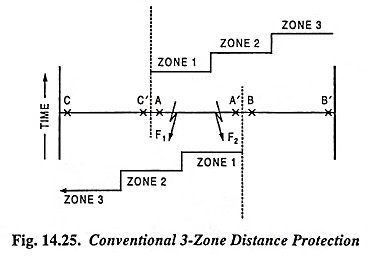
The directional comparison carrier pilot relay schemes presently employed are built around standard three-zone step type distance relays. This speeds up fault clearance for internal zone 2 faults. The carrier channel is employed either for transmission of a stabilizing signal preventing tripping of a remote circuit breaker in the event of a local external zone 2 fault, or for providing a tripping signal in the event of an internal zone 2 fault. The principal features of plain 3-zone carrier aided distance protection Scheme schemes are shown in Fig. 14.25.
Carrier signalling is concerned with the end zones of a protected section A A’. Let the faults occur at points F1 and F2 respectively. Fault at point F1 will be seen at end A in zone 1 and at end A’ in zone 2. Similarly a fault at point F2 will be seen at end A’ in zone 1 and at end A in zone 2.
Transfer trip or intertrip technique is employed for speeding up the fault clearance at the end which clears the fault in zone 2. This is achieved by control of the carrier transmitter and a carrier receive relay by zone 1 contact. For a fault at point F1 the zone 1 relay at end A initiates a carrier signal in addition to completing the zone 1 trip circuit of this end. Carrier signal on reaching end A’ trips it immediately by shunting the zone 2 timer contacts with the help of a carrier receiver relay. A fault at point F2 is also cleared in the same way.