Control of Electric Motor Articles:
Control of DC Electric Motor: A separately excited DC Electric Motor is very versatile as a variable speed motor. Its speed can be varied by varying the applied voltage to the armature or field current. The speed control using the variation … (Read More)
3 Phase Induction Motor Construction: A converter fed 3 Phase Induction Motor Construction has the following advantages over a line fed motor: 1.Smooth start up is guaranteed by variable frequency starting from a low 2.Soft starting and acceleration at constant current and torque … (Read More)
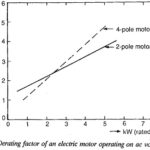
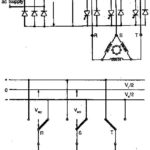
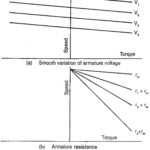
Derating Factor of an Electric Motor Operating on AC Voltage Controller: Typical derating factor of an induction motor fed from a voltage controller are shown in Fig. 4.5(d) when the motor drives a fan or pump loads (T α N2). The … (Read More)
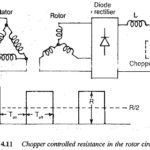
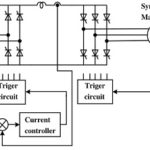
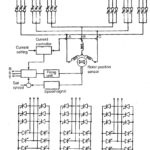
Chopper Resistance in the Rotor Circuit: Speed control by means of slip variation can be achieved by employing a variable resistance Chopper Resistance in the Rotor Circuit. From the equations it is clear that the maximum value of torque does not … (Read More)
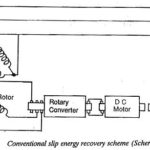
Speed Control Using Slip Energy Recovery Schemes: The foregoing discussion makes it very clear that the methods of voltage control and rotor resistance control have poor efficiency, particularly at low speeds, and find limited application. The Slip Energy Recovery Schemes is … (Read More)
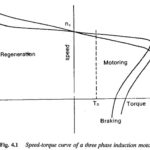
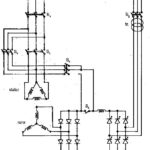
Braking and 4 Quadrants Operation: Subsynchronous converter cascades have been used, till now, in applications requiring one quadrant operation. These can be employed for drives where at least one electrical braking is required. A 4 Quadrants Operation can also be made … (Read More)
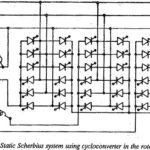
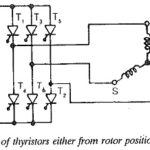
Static Scherbius Drive: The main limitation of the Kraemer drive discussed is the operation at sub-synchronous range due to diode rectifier. Super synchronous speeds can be achieved if the power is fed to the rotor from the ac mains. This can … (Read More)
Speed Control of Variable Frequency Induction Motor: Speed Control of Variable Frequency Induction Motor of a squirrel cage induction motor can be controlled very effectively by varying the stator frequency. Further, the operation of the motor is economical and efficient, if … (Read More)
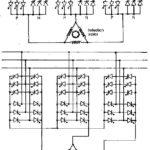
Cycloconverter Feeding Three Phase Induction Motor Drive: Variable frequency supply to an induction motor may be obtained by using a cycloconverter. As has already been discussed, a cycloconverter is a single stage frequency conversion device which converts ac line frequency to … (Read More)
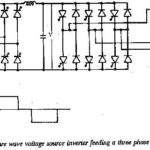
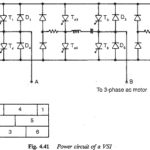
Square Wave Voltage Source Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive: Square Wave Voltage Source Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive is a kind of dc link converter, which is a two stage conversion device. A three phase supply is first rectified using a … (Read More)
PWM Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive: Voltage control in the square wave inverter has been external to the inverter, by means of a phase controlled rectifier on the line side. This posed some practical application problems on the drive by limiting … (Read More)
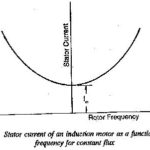
Current Source Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive: Current Source Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive – In a voltage source inverter fed induction motor the applied voltage to the stator is proportional to the frequency, with a correction for the stator resistance … (Read More)
Synchronous Motor Drives: Variable frequency drives employing synchronous motor are receiving considerable interest, and are even becoming competitors to both induction motors and dc motors. These are popular as drives for very high power applications, such as pumps, fans, conveyors, etc. … (Read More)
Synchronous Speed on Variable Frequency Supply: As has already been discussed, the speed of a synchronous motor can be varied by supply frequency variation similar to an induction motor. The applied voltage must be varied in this case also to have … (Read More)
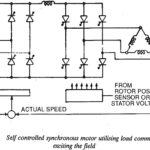
Voltage Source Inverter Fed Synchronous Motor Drive: An inverter fed synchronous motor has been very popular as a converter motor in which the synchronous motor is fed from a CSI having load commutation. Of late more attention is being paid towards … (Read More)
Three Phase Synchronous Motor Fed From Cycloconverter: DC link converter is a two stage conversion device which provides a variable voltage, variable frequency supply. Variable voltage, variable frequency supply can be obtained from a cycloconverter which is a single stage conversion … (Read More)
Current Source Inverter Fed Synchronous Motor Drive: A synchronous motor draws a stator current which is independent of stator frequency when V/f and E/f are maintained constant and armature resistance is neglected. The motor also develops constant torque. The flux also … (Read More)
Current Source Inverter with Forced Commutation: Current Source Inverter with Forced Commutation – As has already been discussed, the disadvantages of machine commutation are (a) limitation on the speed range (b) the machine size is large and due to overexcitation it is … (Read More)
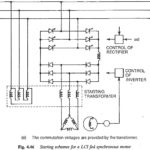
Starting Methods of Synchronous Motor for LCI: It has been pointed out that a Starting Methods of Synchronous Motor for LCI, even though complicated in its construction, has an advantage that it can provide the necessary reactive power required by the … (Read More)
Torque Equation of DC Motor: When dc voltage is applied to the armature of a dc motor with its field excited by dc, a torque is developed and the armature rotates. It accelerates to a speed at which the emf induced … (Read More)
Performance of DC Motors Operating on Phase Controlled Converters: The nature of the output voltage and output current of a phase controlled converters impains the performance of the dc motor operating on these converters. The output of the converter is in … (Read More)
Commutation in DC Motor: Commutation and commutator wear and tear of the dc motor must be given due consideration when the motor operates on solid state converters. Spark-less commutation must be aimed at. The reactance voltage and dynamically induced voltage in … (Read More)
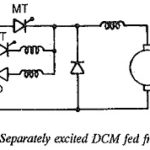
Single Phase Separately Excited DC Motor Drives: The circuit arrangement of a Single Phase Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Drives fed from a single phase controlled converter is shown in Fig. 4.56. The block 1 can be any one of the … (Read More)
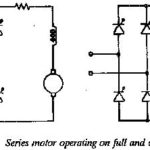
Single Phase DC Series Motor Drives: In the Single Phase DC Series Motor Drives the field is connected in series with the armature. The field current is the same as the armature current. The schematic of a Single Phase DC Series … (Read More)
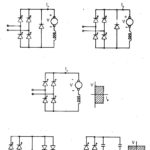
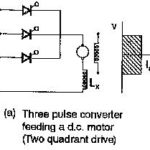
Three Phase Drives: Single phase drives discussed in the previous section are employed for low and medium powers. When the power of the drive is very large the three-phase converter is preferred for supplying the load. As has been described early … (Read More)
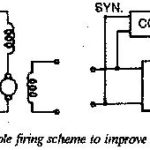
Methods to Leading Power Factor: We have seen that a phase controlled converter requires reactive power for control and commutation. The harmonics do not contribute to the active power loading but they contribute to the reactive loading of the line. Because … (Read More)
Chopper Fed DC Drives: The variable voltage to the armature of a dc motor for speed control can be obtained from a dc chopper which is a single stage dc to dc conversion device. The voltage variation at the load terminals … (Read More)
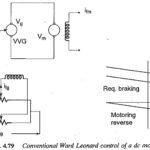
Reversible Drives using Phase Controlled Converters: When speed control in both forward and reverse directions is required a Reversible Drives is used. In several applications the speed reversal may be required very frequently in which case a regenerative reversal may be … (Read More)
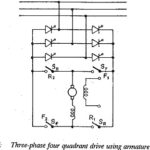
Reversible Drive using Armature Current Reversal: A schematic of a reversible drive using contactors to reverse the Armature Current Reversal for reversing the rotation is shown kin Fig. 4.81. The contactors F1 and F2 are provided for rotation in the forward direction, … (Read More)
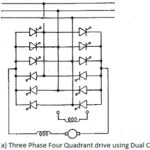
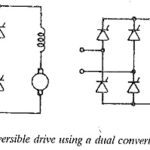
Reversible Drive using Dual Converter: It is possible to reverse both voltage and current of the load using a dual converter. The current reversal is very fast in this case as the system is static without the mechanical output. A Reversible … (Read More)
Reversible Drive using Field Reversal: A Reversible Drive using Field Reversal can be realised as shown in Figs. 4.83 and 4.84. In Fig. 4.83, the armature is fed from a two quadrant converter with change over mechanical contactors in the field, … (Read More)
Reversible Drives using Choppers: Using two quadrant choppers a reversible drive can be achieved, because this combination allows reversal of both current and voltage of the motor terminals. We can get a regenerative reversible drive. The motor can operate in all … (Read More)