CSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive:
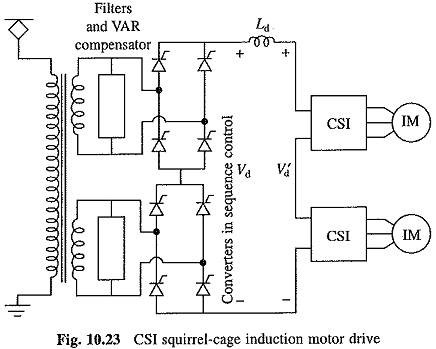
Performance and operation of CSI induction motor drive is already explained . Figure 10.23 shows details of the traction drive of CSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive.
In a multistage converter ac is converted into dc with sequence control to improve converter power factor and to reduce harmonics produced by it.
Filters and static VAR compensators are used to maintain power factor above 0.8 and to Keep the harmonics within acceptable limits Current source inverter (CSI) converts dc into variable frequency current which is then fed to the induction motor. Each motor is fed from a separate CSI.
Since CSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive are not suitable for parallel operation, they are connected in series. When four motors are employed, one alternative will be to connect all the four inverters in series, each feeding its own motor. A single converter in sequence control then feeds all the four inverters.
Another alternative will be to connect two inverters in series powered by one sequence controlled converter (Fig. 10.23). Two such pairs, each consisting of two inverters fed from one sequence controlled converters, are then supplied from a common transformer. The current source inverter has already shown. At low speeds pulsewidth modulation is sometimes employed to achieve a smooth start.
Regenerative braking capability is inherent in the drive. For this inverter frequency is reduced to shift motor operation from motoring to braking and the converter is operated as inverter.
The CSI Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Drive has following features:
- Bulky, heavy and expensive.
-
Poor adhesion due to slow dynamic response and series connection.