CT Scan Working Principle:
CT Scan Working Principle – Biomedicine is one area in which the use of digital signal processing techniques had had great impact.
Computer tomography
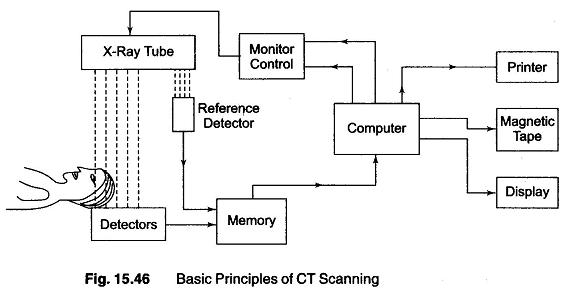
A recent advance in diagnostic analysis is represented by computer tomography (CT) scanning. While in standard radiography (X-rays) a 3-dimensional object (part of the body) is represented on a plane (film), in CT the 3-D structure can be recovered. The basic idea of CT Scanning is shown in Fig. 15.46.
A moving scanning system, including an X-ray source, collimators and detectors, rotates around a part of the patient’s body, taking many readings of X-ray transmissions across the analysed part (e.g. the head). These readings are then sent along with the output of a reference detector to a large memory disk and to a computer, which through a suitable software program reconstructs a cross-section of the analysed part. The processing done by the computer is essentially a 2-D (image) reconstruction from a 1-D projection.
The use of digital filtering and FFT techniques is vital for various reconstruction techniques of images from their projections, known as Analytical reconstruction techniques.