DC Motor Drives Articles:
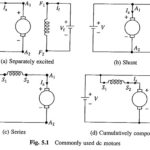
Types of DC Motor: The commonly used Types of DC Motor are shown in Fig. 5.1. In a separately excited motor, the field and armature voltages can be controlled independent of each other. In a shunt motor, field and armature are … (Read More)
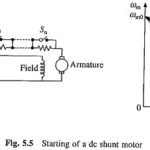
DC Shunt Motor Starter Design: Maximum current that a DC Shunt Motor Starter Design can safely carry during starting is limited by the maximum current that can be commutated without sparking. For normally designed machines, twice the rated current can be … (Read More)
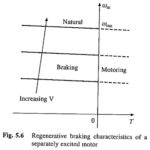
DC Motor Braking Methods: The need for electric braking was explained earlier, the motor works as a generator developing a negative torque which opposes the motion. Three types of DC Motor Braking Methods are Regenerative braking; Dynamic or Rheostatic braking; and Plugging or … (Read More)
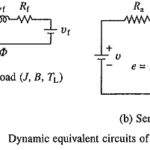
Transient Analysis of DC Motor: Starting, braking, reversing speed changing and load changing are the Transient Analysis of DC Motor which commonly occur in an industrial drive. One is interested in knowing how current, torque and speed of the driving motor … (Read More)
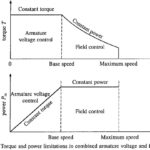
Speed Control of DC Motor Drives: The Speed Control of DC Motor Drives can be any of the following methods: Armature voltage control Field flux control Armature resistance control Speed-torque curves of dc motors for these methods of speed control are shown in Figs. 5.16 … (Read More)
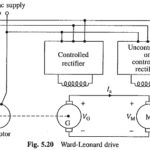
Ward Leonard Method of Speed Control: Known after the name of its inventor Ward Leonard Method of Speed Control (1891), it consists of a separately excited generator feeding the dc motor to be controlled. The generator is driven at a constant … (Read More)
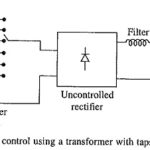
Armature Voltage Control using Transformer: Variable voltage for the dc motor control can also be obtained by either using an auto-transformer or a Armature Voltage Control using Transformer with tappings (either on primary or on secondary) followed by an uncontrolled rectifier … (Read More)
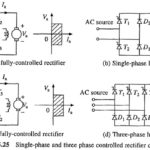
Controlled Rectifier Fed DC Drives: Controlled Rectifier Fed DC Drives are used to get variable dc voltage from an ac source of fixed voltage. Controlled Rectifier Fed DC Drives are also known as Static Ward-Leonard drives. Figure 5.25 shows commonly used Controlled … (Read More)
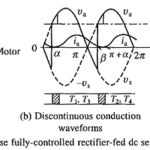
Single Phase Fully Controlled Rectifier Control of DC Motor: The Single Phase Fully Controlled Rectifier Control of DC Motor is shown in Fig. 5.26(a). Motor is shown by its equivalent circuit. Field supply is not shown. When field control is required, … (Read More)
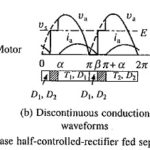
Single Phase Half Controlled Rectifier Control of DC Separately Excited Motor: Single Phase Half Controlled Rectifier Control is shown in Fig. 5.29(a). In a cycle of source voltage defined by Eq. (5.71), T1 receives gate pulse from α to π and T2 … (Read More)
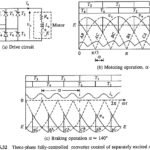
Three phase Fully Controlled Rectifier Control of DC Separately Excited Motor: Three phase Fully Controlled Rectifier Control (6 pulse) fed separately excited dc motor drive is shown in Fig. 5.32(a). Thyristors are fired in the sequence of their numbers with a … (Read More)
DC Motor Reversing Switch Diagram: DC Motor Reversing Switch Diagram is shown in Fig. 5.34(a). A fully-controlled rectifier feeds the motor through a reversing switch RS which is used to reverse the armature connection with respect to the rectifier. A fully-controlled … (Read More)
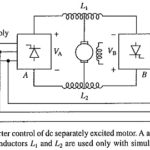
Dual Converter Control of DC Separately Excited Motor: A Dual Converter Control of DC Separately Excited Motor (Fig. 5.35) consists of two fully-controlled rectifiers connected in anti-parallel across the armature. For power ratings upto around 10 kW, sigle-phase fully-controlled rectifiers can … (Read More)
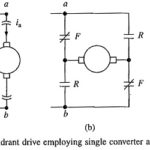
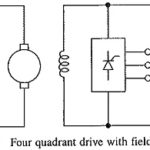
Four Quadrant Drive With Field Reversal: Four Quadrant Drive With Field Reversal as shown in Fig. 5.36, armature is fed from a fully-controlled rectifier and the field from a dual converter so that field current can be reversed. With field current … (Read More)
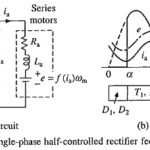
Rectifier Control of DC Series Motor: Single-phase controlled Rectifier Control of DC Series Motor are employed in traction. A single-phase half-controlled Rectifier Control of DC Series Motor is shown in Fig. 5.37(a). Equivalent circuit of motor is also shown. Since back … (Read More)
Drawbacks of Rectifier Fed DC Drives: Drawbacks of Rectifier Fed DC Drives are as follows: 1. Distortion of Supply: Source current of a rectifier has harmonics. In a weak ac source, with high internal impedance, current harmonics distort source voltage. Furthermore, temporary short … (Read More)
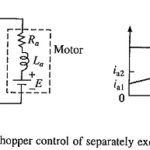
Chopper Control of Separately Excited DC Motor: Motoring Control : A transistor Chopper Control of Separately Excited DC Motor drive is shown in Fig. 5.41(a). Transistor Tr is operated periodically with period T and remains on for a duration ton. Present … (Read More)
Chopper Control of Series Motor: Motoring : Chopper Control of Series Motor and va and ia waveforms will be same as shown in Fig. 5.41. Va is given by Eq. (5.113). However, e is not constant but varies with ia. Due to saturation of … (Read More)
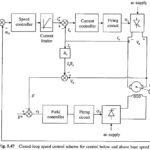
Closed Loop Speed Control of DC Motor: The converters (rectifiers and choppers) are built using semiconductor devices, which have very low thermal capacity. Consequently their transient and steady state current ratings are same. … (Read More)