Diesel Engine Power Plant – Layout, Types and Applications:
Introduction: Diesel engine power plant (prime mover is a diesel engine) are installed where supply of coal and water is not available in sufficient quantity. These plants produce power in the range of 2 to 50 MW. The diesel power plants are more efficient then any other heat engines of comparable size. It is cheap in cost. It can be started quickly and brought into the service. The diesel engine power plant will provide the most economic means of generating electricity on small scale particularly where there is no convenient site for micro hydro power plants, cheap fuels are not available and load factors are considerably large.
Application:
- Suitable for small or medium capacity range of 2 to 50 MW.
- Used in industries where power equipment’s is up to 500 kW.
- Used as standby plants to hydro and steam power plant.
- Used as mobile power generation system such as automobile, ship, aeroplane, railways and road transport.
- Used as peak load plants in combination with thermal or hydro-plants to meet the power demands during peak hours.
Site selection:
- Site selection for the diesel power plant should be nearer to the load centre; this is to reduce the cost of transmission of power and also reduce the power loss.
- The site for the diesel power plant should be nearer to the source of fuel supply, to decrease the transportation charges.
- The site for the diesel engine power plant should be far away from the town, thus smoke and flue gases released from the plant will not affect human life.
- Sufficient quantity of water should be available at the site selected.
- The selection of the site for the plant should be in such a way that, it has road and rail transportation facilities.
Advantages:
- Diesel engine power plant can be located at any place.
- The quantity of the water required for these plants for cooling is less.
- Power plant is simple in design and diesel fuel is easy to handle.
- Less fuel storage space.
- It can be started quickly.
- Longer life than steam power plant.
- High thermal efficiency than steam power plant.
- Requires no operating staff.
Disadvantages:
- Diesel fuel is costly.
- Cost of lubrication is very high.
- Maintenance charges are generally high.
- Limited capacity about 50 MW of power.
- Not suitable for overload condition.
- In a diesel engine power plant noise is a serious problem.
Types of Diesel Engine Power Plant:
Diesel power plants are mainly classified as stationary diesel power plants and mobile diesel power plants.
Stationary units use two-stroke (or) four-stroke diesel engines coupled with synchronous generators. These units are considered average in their power rating if the rating does not exceed 750 kW. Large diesel plants have power ratings of 2,200 kW or more. These plants are mainly used in areas remote from transmission lines and where the construction of steam (or) hydro-electric power plant is not feasible.
Mobile diesel power plants can be used as main auxiliary or stand by power source. They are widely used in agriculture, transportation, forestry and by expeditions involving geological exploration.
The diesel electric power-plants are classified based on their applications as follows:
1. Peak load plant
When there is high demand for electricity, diesel power plants are used in combination with thermal or hydro-plants as peak load plants. Peak loads can occur in the evening after work hours when household appliances are heavily used or during summer months when the air-conditioning load is high. Diesel power plant is particularly preferable as peak load plant as it can be started quickly and it has no standby losses as in the case of thermal plants where boilers always must be kept hot.
2. Mobile plants
Mobile diesel plants can be used for temporary or emergency purposes such as for supplying power to large civil engineering works for supplementing electricity supply systems that are temporarily short of power. They are mounted on skids or trailers and transported to the required site.
3. Stand-by Units
Diesel plants can be used as standby units to supply part load when required. For example, a diesel plant can be used with a hydro-plant as a stand-by unit, if the water available is not sufficient due to reduced rainfall. Here the diesel unit supplies power in parallel with the hydro-power plant. The diesel unit is used temporarily till sufficient water is available to take the full load.
4. Emergency plant
The plants are normally idle but are used for emergency purposes where power interruption would mean financial loss or danger such as in key industrial processes, tunnel lighting and operating rooms of hospitals. Under emergency conditions, these plants are also used for telecommunication and water supply.
5. Nursery station
When a temporary power plant is required to supply the power to a small town until the main grid is available, it is known as “Nursery Station“. A Nursery station can be moved to another area which needs power on a small scale. A diesel power plant is suitable for this purpose.
6. Starting Stations
Small diesel units can be used for starting purposes of large steam plants. These units run the auxiliaries initially for starting, after which they are disconnected.
7. Central stations
In places where the capacity required is small (5 to 10 MW), Diesel units can be used as central stations, such as for commercial purposes and public utilities e.g., cinema hall, hospital and municipalities. The capacity limits of the plant generally decided by the cost of the plant and local conditions regarding the availability of fuel and water, space requirements and non-availability of the grid.
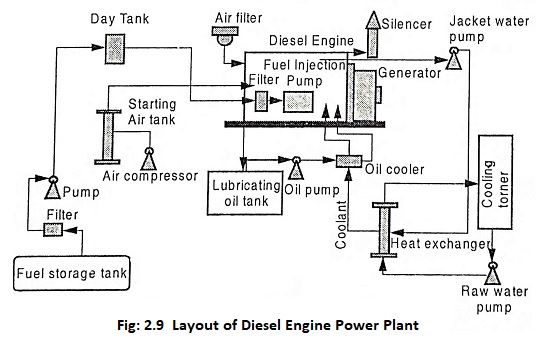
Layout of Diesel Engine Power Plant:
The essential components of a Diesel power plant are:
(i) Diesel engine
It is a compression ignition engine. They are generally two stroke or four stroke cycle engines. Air is admitted into the cylinder of the engine and is compressed. At the end of compression stroke, fuel (Diesel) is injected. The burnt gases, expand and do work on piston. The engine is directly coupled to the generator. These gases from the cylinder are then exhausted to the atmosphere.
(ii) Engine starting system
This system contains an air compressor and a starting air tank. This system starts the Diesel engine of a Diesel power plant “under cold condition”.
(iii) Fuel system
The fuel is delivered to the plant gate by trucks, rail barge (or) and by tankers and stored in the fuel storage tank. The piping equipment with the necessary heaters, by passes, drain lines, relief valves, strainers and filters, flowmeter and temperature indicator are arranged in a proper manner to make the main flow workable and practical. The tank should contain a manhole for internal access like repair, cleaning, etc. After purification, the fuel is supplied to the system (Engine). A day tank (fuel from the storage tank is pumped to the day tank) provides fuel to the engine for daily usage. The day tank is placed high so that fuel flows to the engine naturally due to gravity.
(iv) Air intake system
Air intake system supplies air into the combustion chamber of the diesel engine for burning fuel. Air filter is used to remove dust from the incoming air. Air filters may be dry type, which are made of wool or cloth. In wet filter, an oil bath is used to remove the dust particles. Here air is swept over or through the oil bath so that the dust particles get coated with oil. Following care should be taken while constructing suitable air intake system.
- Air intake should not be located inside the engine room.
- Air intake filters should not be located in an in accessible location.
- The purpose of an air intake system is to clean and silence the incoming air and supply it for super charging.
(v) Exhaust system
The exhaust system is used to discharge the engine exhaust to the atmosphere. The exhaust pipe should be short in length with minimum number of bends. It should be capable to bear the engine vibration. To reduce high level velocity noises, silencers must be installed. If required, provision has to be made to extract heat from the exhaust for fuel heating or process heating.
(vi) Engine cooling system
The temperature of the fuel burning in the engine is in the range of 1500°C to 2000°C. If the engine is run without proper cooling, chances of distortion of engine parts and burning of lubricating oil may occur due to over heating. On the other hand, if the temperature is too low, the lubricating oil will not spread properly which causes wearing of engine parts like piston and cylinder. So, apart from absorbing and dissipating heat from the engine, the cooling system should also maintain sufficient operating temperature for the smooth and efficient operation of the engine.
To reduce the temperature, water is circulated through water jackets positioned around the combustion chamber.
The hot water leaving the jacket is passed through the heat exchanger. In the heat exchanger, the raw water drains the heat from jacket water and is cooled in the cooling tower.
Engine cooling systems are classified into three types.
- Air cooling system
- Water cooling system
- Oil cooling system
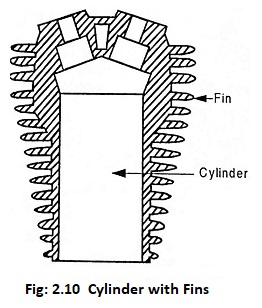
(a) Air cooling system
It is generally used in small engines. In this system, fins or extended surfaces are provided on the cylindrical walls and cylindrical head. Heat generated due to combustion in the engine cylinder will be conducted to the fins and when the air flows over the fins, heat will be dissipated to air.
(b) Water cooling system
In this, cooling is provided around the cylinder walls and head. They are two types of water cooling system.
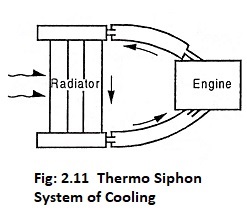
- Thermo Siphon system
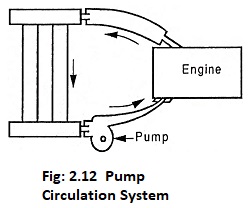
- Pump circulation system
- Thermo Siphon system
In this system, the circulation of water is due to difference in temperature of water. So in this system pump is not required.
- Pump circulation system
In this system, the circulation of water is by means of pump.
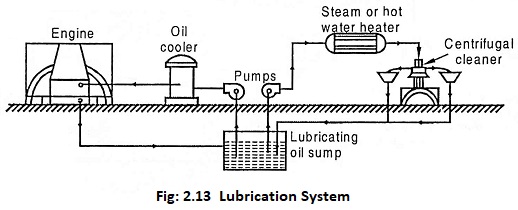
(vii) Lubrication system
Lubrication is necessary to prevent the wear and tear of engine parts caused by frictional forces due to rubbing of part surfaces while engine running. The effectiveness of the lubricating system determines the life of the engine and the overall efficiency of the plant. Lubricants of liquid, solid and semi-solid types are available of which liquid oil lubricants are most commonly used. All moving parts of the system are lubricated with the piston and cylinder requiring special lubricant as they operate under condition of high pressure and temperature.
Generally forced feed lubrication system is used which consists of pump, oil cleaners, oil coolers, storage, sump tanks and safety devices. Lubricating oil should be purified before circulating into the system which can be done by various methods like settling, centrifuging, filtering and chemical reclaiming. In these methods centrifuging gives excellent purification and hence it is widely used. The Fig.2.13 shows a schematic of the lubricating system used in diesel power plants.
(viii) Starting system
Diesel engines are generally started by some mechanical system as they are difficult to be started by hand cranking due to the high compression required. So, various methods using compressed air, electric motors and auxiliary gasoline engines are employed for the starting of a diesel engine, of these methods, the compressed air system is commonly used.
- Compressed air system
In an multi-cylinder engine, compressed air at a pressure of about 20 bar admitted to a few cylinders which causes the engine crank shaft assembly to rotate. Gradually the engine gains momentum and the engine is started by supplying the fuel. This system is used in big diesel power plants.
- Electric starting
In this system, an electric motor is used to rotate the engine shaft by a gear arrangement. Supplying fuel to the engine will start and the electric motor disengages automatically. Electric starting system is simple and effective. For small diesel engines, a storage battery is used to supply power to the electric motor.
- Starting by an Auxiliary Engine
In this system, a petrol engine is first started by hand cranking. This engine is connected to the diesel engine by clutch and gear arrangements and so, by gradually engaging the clutch, the diesel engine is started. After starting, the clutch is automatically disengaged.
(ix) Governing system
Different loads are experienced by the power plant over different time periods. The function of the governing system is to maintain constant speed of the diesel engine irrespective of the load on the plant. This is done by varying the quantity of fuel supplied to the engine according to the load. Centrifugal type governor is generally used for this purpose.