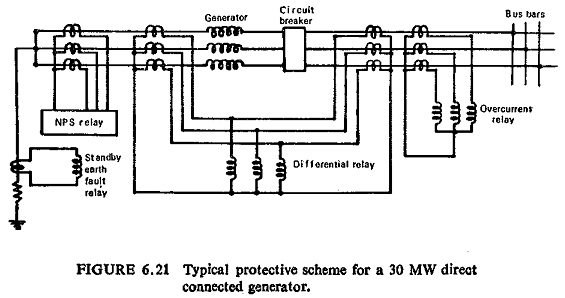
Direct Connected Generator Protection:
Direct connected generators are normally of smaller ratings and a typical scheme of Direct Connected Generator Protection for a 30 MW generator is shown in Fig. (6.21).
It consists of the following protections:
-
Unbiased differential protection.
-
Backup overcurrent protection.
-
Negative phase sequence protection.
-
Standby earth fault.
In addition to these protections the following may also be provided:
-
Field failure protection.
-
Rotor earth-fault protection.
-
Reverse power protection (to be provided on back pressure turbine sets and engine driven sets).
Relay Tripping Functions:
The various systems have been described simply as means of operating the protective relays whose function is to energize a multi contact tripping relay, which in turn operates the following:
- The main circuit breaker to isolate the generator from the system.
- The neutral earthing switch, if any, to interrupt earth-fault current.
- The field switch to begin the decay of the generated voltage feeding the fault, in some cases by switching in a suppression resistor.
- An alarm relay.
Relays on the unit transformer LV side trip only the unit transformer, leaving the generator in service. The auxiliary protections energize the alarm relay.