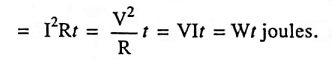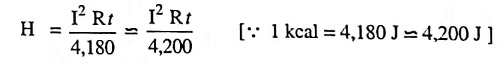Electric Heating Interview Questions and Answers:
1. Why electric heating is preferred over other forms of heating ?
Ans. Electric heating is preferred over other forms of heating because of its numerous inherent advantages like economy, cleanliness, absence of flux gases, easy of control, automatic protection, upper limit of temperature, special heating needs.
2. What is an oven ?
Ans. Low temperature heating chamber with provision for ventilation is termed as oven.
3. Write and explain Joules law of electric heating.
Ans. According to Joule’s law of electric heating, the energy expended or heat generated in joules is given as
Work done or heat generated
i.e., According to Joules law of heating, heat produced in an electric circuit of resistance R and carrying current I for t seconds is
(i) proportional to the square of the current i.e., H ∞ I2
(ii) proportional to the resistance of the circuit i.e., H ∞ R, and
(iii) proportional to the time duration for which the current flows through the circuit i.e., H ∞ t
Heat produced in kcals,
4. What properties are considered for selecting material for heating element ?
Ans. The properties to be considered in selection of material for heating elements are resistivity, melting point, temperature coefficient of resistance, and freedom from oxidation.
5. What are the essential properties of resistance heating elements ?
Ans. The essential properties of resistance heating elements are : High resistivity, high melting point, low temperature coefficient of resistance and freedom from oxidation.
6. Name few materials, that are widely used as heating element materials.
Ans. The materials widely used as materials for heating elements are nickel-chromium (Nichrome) alloy, Ni-Cr-Fe alloy, nickel-copper alloy (Eureka or constantan), iron-chromium-aluminium alloy (Kanthal) and alloys containing iron, chromium, cobalt and aluminium.
7. What are the causes of failure of heating elements ?
Ans. The chief causes of failure of heating elements are formation of hot spots, oxidation and intermittency of operation, embrittlement due to grain growth, contamination and corosion.
8. Name few applications of infrared heating.
Ans. Infrared heating finds applications in (i) paint stoving (ii) drying of radio-cabinets and wood furniture (iii) preheating of plastics prior to moulding (iv) softening of thermo-plastic sheets, (v) drying of pottery, paper, textiles etc. where moisture content is not large.
9. Name the types of electrodes used in arc furnaces.
Ans. The electrodes used in arc furnaces are of three types namely carbon, graphite and self-baking electrodes.
10. Why are indirect arc furnaces not built in large sizes ?
Ans. The arc is produced between two electrodes and heat is transferred to the charge by radiation only. Such construction limits the use of single phase supply. The size of the furnace is thus limited by the amount of single-phase load, which can be taken from one point.
11. How is power input to submerged arc furnace controlled ?
Ans. The power input to submerged arc furnace is controlled by varying distance between electrodes or by varying the voltage applied to the electrodes.
12. How is control of power affected in electric arc furnaces ?
Ans. The power input to arc furnaces can be controlled by raising or lowering the electrodes or by varying the voltage applied
to the arc furnace (by changing of tapping on supply transformer); preferably both voltage and electrode controls.
13. At what power factor would you like to operate the electric arc furnace ?
Ans. At power factor of about 0.9, but not below 0.8 in any case.
14. What type of supply is used for direct core type induction furnace in our country ?
Ans. Single-phase, 50 Hz, 600 V supply is used for direct core type induction furnaces.
15. How amount of heating is controlled in high frequency eddy current heating ?
Ans. The amount of heating is controlled by controlling the supply frequency and the flux density in high frequency eddy current heating.
16. What are the applications of high frequency eddy current heating ?
Ans. The applications of high frequency eddy current heating are surface hardening, annealing, soldering, welding, drying of paints, melting of precious metals, sterilization of surgical instruments and forging of bolt-heads and rivet heads.
17. How can the rate of dielectric heating be varied ?
Ans. Rate of dielectric heating can be varied by varying either supply voltage or supply frequency.
18. Why dielectric heating is employed only where other methods are impracticable or too slow ?
Ans. Because of very high cost of equipment required for dielectric heating.