Electric Voltage:
Electric Voltage states that, according to the structure of an atom, we know that there are two types of charges: Positive and Negative. A force of attraction exists between these positive and negative charges. A certain amount of energy (work) is required to overcome the force and move the charges through a specific distance.
All opposite charges possess a certain amount of potential energy because of the separation between them. The difference in potential energy of the charges is called the Potential Difference.
Potential Difference in electrical terminology is known as Electric Voltage, and is denoted either by V or υ. It is expressed in teams of energy (W) per unit charge (Q); i.e.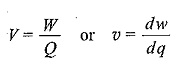
where
- dw is the small change in energy,
- dq is the small change in charge,
- energy (W) is expressed in joules (J),
- charge (Q) in coulombs (C), and
- voltage (V) in volts (V).
Define One Volt:
One volt is the potential difference between two points when one joule of energy is used to pass one coulomb of charge from one point to the other.