Fast Recovery Diode (FRD):
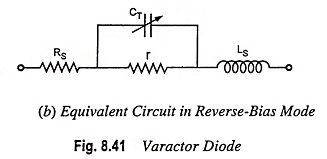
Fast recovery diode are designed to provide ultrahigh switching speed. The devices can be classified into two types : diffused P-N junction diodes and metal semiconductor diodes. The equivalent circuit of both types can be represented by the varactor diode [Fig. 8.41 (b)].
The total recovery time for a P-N junction diode can be substantially reduced by introducing efficient recombination centers, such as Au and Si, to the bulk material. Although the recovery time is directly proportional to the lifetime τ, it is not possible, unfortunately, to reduce recovery times to zero by introducing an extremely large number of recombination centers, because the reverse generation current of a P-N junction is proportional to recombination centres.
For direct band gap semiconductors, such as GaAs, the minority-carrier lifetimes are much smaller than that of silicon. This results in ultrahigh speed GaAs P-N junction diodes with recovery times of the order of 0.1 ns or less.
For silicon, the practical recovery time is in the range of 1 to 5 ns. The metal semiconductor diode (Schottky diode) also exhibits ultrahigh speed characteristics, because most Schottky diodes are majority-carrier devices and the minority-carrier storage effect is negligible.