Feeder Protection Relay Articles:
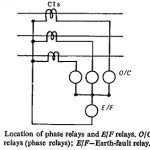
Types of Feeder Protection Relay: A composite transmission system may use one or more of the following types of Feeder Protection Relay. Overcurrent Protection: This is of two types: (i) nondirectional time and current graded schemes; (ii) directional time and current graded … (Read More)
Overcurrent Protection of Feeders: Overcurrent relays offer the cheapest and the simplest protection for lines. The maximum load currents must be known to determine whether the ratio of the minimum fault current to maximum load current is high enough to enable … (Read More)
Overcurrent Earth Fault Protection: Earth-fault protection can be provided with normal overcurrent relays, if the minimum earth-fault current is sufficient in magnitude. The magnitude of earth-fault current is usually low compared to the phase-fault currents because … (Read More)
Directional Earth Fault Relay: In the case of Directional Earth Fault Relay the angular relationship of residual current and residual voltage is independent of the faulted phase and is governed only by the R/X ratio of the fault path. The current … (Read More)
Principle of Distance Relaying: The Principle of Distance Relaying is governed by the ratio of voltage to current at the relay location and the operating time of the relay automatically increases with an increase of this ratio. Now the impedance or … (Read More)
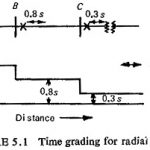
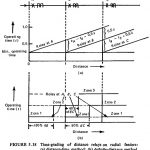
Time Grading of Distance Relay: Two methods of Time Grading of Distance Relay are shown in Fig. (5.18). First Method is the distance time method at (a) has the operating time increasing steadily with increasing distance between the relay location and … (Read More)
Fault Resistance Calculation: Fault Resistance Calculation consists of two components, the resistance of the are and the resistance of earth. The second component is present only when it involves an earth-fault. In such a case the resistance of earth would mean … (Read More)
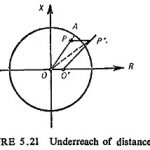
Reach of Distance Relay: A distance relay is set to operate up to a particular value of impedance; for an impedance greater than this set value the relay should not operate. This impedance, or the corresponding distance is known as the … (Read More)
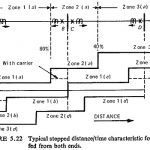
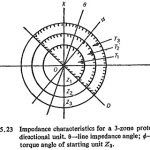
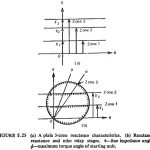
Scheme of Distance Protection: In developing an overall Scheme of Distance Protection, it is necessary to provide a number of relays to obtain the required discrimination. Modern practice is to adopt definite distance method of protection applied in 3 zones (steps). A … (Read More)
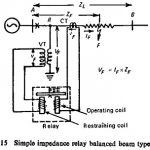
Distance Protection Impedance Relay: It has already been pointed out that the impedance is directly proportional to the length of the line, and hence an impedance relay which measures impedance can be used to recognise a … (Read More)
Distance Protection by Reactance Relays: Like impedance relays, Distance Protection by Reactance Relays are also amplitude comparators and thus require an additional directional unit. Although the performance of reactance relays on single-fed systems is not unduly affected by fault resistance, there … (Read More)
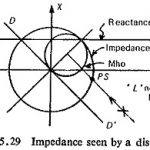
Power Swings in Power System Protection: The impedance measured or seen by a distance relay during normal load is shown in Fig. (5.29). Normally this would be outside the tripping zone of the distance relay, but, on a very long line … (Read More)
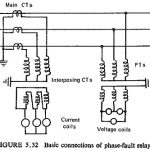
Current and Voltage Connection in Distance Relay: It is essential for the distance relay to measure the same distance between the fault and the relay under any type of fault condition. It is possible to supply the relays so that they … (Read More)
Selection of Distance Relay: The factors to be considered for the Selection of Distance Relay scheme can be enumerated as follows: Speed of operation. Measuring relay characteristics. Fault coverage. Economic considerations. 1. Speed of Operation: Operating time is of great importance on systems which are liable to … (Read More)
Application of 3 Phase System: In a Application of 3 Phase System, a wide variety of faults can occur, i.e. phase to phase, phase to earth, 2 phase to earth and 3 phase fault, various combinations in a Application of 3 … (Read More)
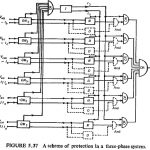
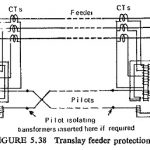
Pilot Wire Protection Relay: In this case the auxiliary Pilot Wire Protection Relay are provided to carry the information signals from one end to the other. Protective systems requiring the use of pilot wires on transmission lines operate on the principle … (Read More)
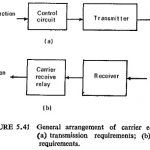
Carrier Pilot Protection and Microwave Pilot Protection: The problem of providing economically an auxiliary channel by means of pilots for long lines directed attention to carrier techniques. In this case the power line itself is used as the channel for carrying … (Read More)
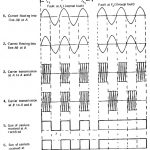
Phase Comparison Carrier Protection: The phase comparison pilot-relaying operates on the principle of comparing the phase position of the currents at the two ends of the protected section. The Phase Comparison Carrier Protection of these currents is made over carrier channels. … (Read More)