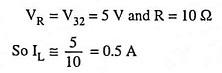Fixed Positive Voltage Regulators:
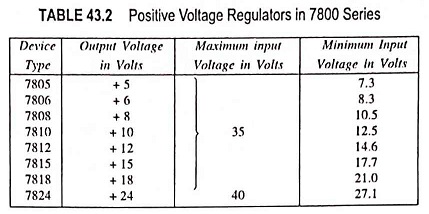
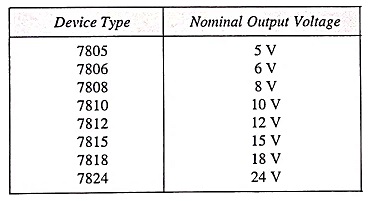
The series 7800 regulators provide eight voltage options, ranging from 5 to 24 V, as indicated in Table 43.2. These ICs are designed as fixed voltage regulators and with adequate heat sinking. Although these devices do not require any external component, such components can be employed for providing adjustable voltages and currents. These Fixed Positive Voltage Regulators ICs also have internal thermal overload protection and internal short-circuit current limiting.
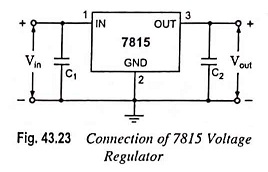
Figure 43.23 illustrates how one such IC, a 7815, is connected to provide voltage regulation with output of + 15 V dc from this unit. An unregulated input voltage Vin is filtered by capacitor C1 and connected to the pin 1 (IN terminal) of IC. The pin 3 (OUT terminal) of the IC provides a regulated + 15 V which is filtered by capacitor C2 (mostly for any high frequency noise). The middle pin (GND terminal) of the IC is connected to ground. While the input voltage may vary over some permissible voltage range, and the output load may vary over some acceptable range, the output voltage remains constant within specified voltage variation limits. These limitations are mentioned in the manufacturer’s specification sheet.
In addition, the minimum difference between input and output voltages (Vin – Vout), called the dropout voltage, must be typically 2.0 V, even during the low point on the input ripple voltage. Furthermore, the capacitor C1 is required if the regulator is located at an appreciable distance from a power supply filter. Even though C2 is not required, it may be used to improve the transient response of the regulator. A table of fixed positive voltage regulators ICs is given in Table 43.2.
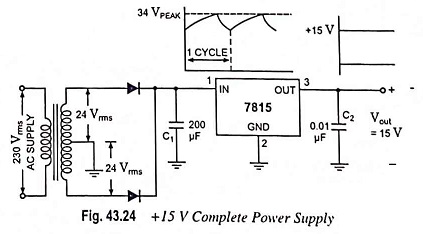
The connection of an IC7815 in a complete voltage supply is shown in Fig. 43.24. The ac line voltage is stepped down to 24 Vrms across each half of the centre-tapped transformer. A full-wave rectifier and capacitor filter then provides an unregulated dc voltage with ac ripple of a few volts as input to the voltage regulator. The IC7815 then provides an output of +15 V dc.
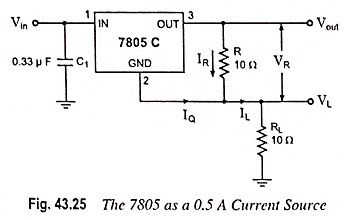
IC7800 regulators can also be employed as current sources. A typical connection diagram of 7805C as a 0.5 A current source is depicted in Fig. 43.25.
The current supplied to the load is given as
when IQ is quiescent current in amperes (4.3 mA typically for IC7805)
In Fig. 43.25,
The output voltage w.r.t. ground is
The load resistance, RL = 10 Ω, therefore VL = 5 V
Thus
Minimum input voltage required, Vin = Vout + dropout voltage
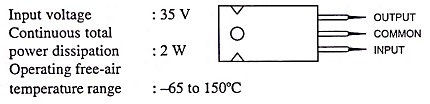
Specifications: The specifications sheet of fixed positive voltage regulators of 7800 series is given below. Some considerations of a few of the more important parameters should be considered.
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
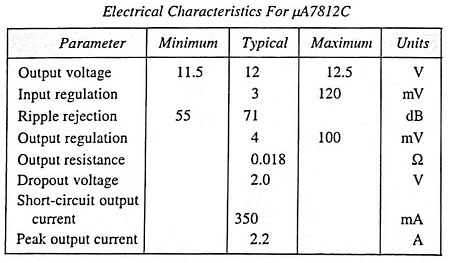
Output Voltage: The specification for IC7812 indicates that its nominal output voltage is 12 V but could be as low as 11.5 V or as high as 12.5 V.
Input or Line Regulation: The input or line regulation is seen to be typically 3 mV, to a maximum of 120 mV.
Output or Load Regulation: The output or load regulation is seen to be typically 4 mV to a maximum of 100 mV (for output currents from 0.25 to 0.75 A). It means that the output voltage can typically vary only 4 mV from the rated 12 V dc.
Short-circuit Output Current: The amount of current is limited to 350 mA if the output were to be short circuited (may be by accident or by another faulty component).
Peak Output Current: The typical peak output current that might be drawn from the supply is 2.2 A against rated maximum current of 1.5 A. It indicates that though the IC is rated as capable of providing 1.5 A, but somewhat more current can be drawn (possibly for a short duration of time).
Dropout Voltage: The dropout voltage, typically 2 V, is the minimum amount of voltage across the input-output terminals that is required to be maintained if the IC is to operate as a regulator. In case the input voltage falls too low or the output rises so that at least 2 V is not maintained across the input-output terminals of IC, the IC will no longer provide voltage regulation. So input voltage is maintained large enough to ensure that the dropout voltage is provided.