Hybrid Parameters Articles:
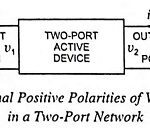
Hybrid Parameters of Transistor or h Parameters and Hybrid Model: A box representing a two-port network is illustrated in Fig. 11.1. The terminal behavior of a two-port device may be specified by two voltages and two currents (voltage v1, and current … (Read More)
Transistor Hybrid Model: The basic assumption in arriving at a transistor linear model or equivalent circuit is that the variations about the operating or quiescent point are small and, therefore, the transistor parameters can be considered constant over the small range … (Read More)
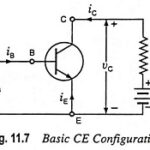
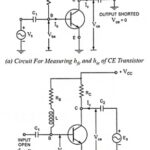
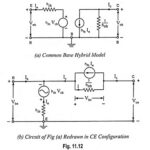
Experimental Determination of Hybrid Parameters: Determination of hybrid parameters of a general linear circuit has already been discussed. For determination of hybrid parameters for a CE transistor, consider the circuits given in Fig. 11.8. The rms values will be considered in … (Read More)
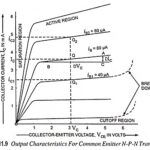
Determination of h Parameters from Static Characteristics: Functional relationships for the CE configuration of total instantaneous collector current and base voltage in terms of two variables (base current and collector voltage) are given from earlier equations respectively. Such functional relationships are … (Read More)
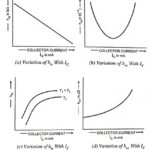
Variations of Hybrid Parameters of a Transistor: The variation of h parameters depends upon junction temperature, collector current and collector-to-emitter voltage VCE. Among these factors, the variations of Hybrid Parameters of a Transistor due to junction temperature and collector current are … (Read More)
Conversion of Hybrid Parameters in Transistor Three Configurations: Some transistor manufacturers provide only the four CE hybrid parameters while others provide CB hybrid parameters. Sometimes, for a specific purpose, it becomes necessary to convert one set of h parameters in one … (Read More)