Induction Motor Drives Articles:
Three Phase Induction Motors: Three Phase Induction Motors are of two types: squirrel-case and wound-rotor. In squirrel-cage, the rotor consists of longitudinal conductor-bars shorted by circular connectors at the two ends while in wound-rotor motor, the rotor also has a balanced … (Read More)
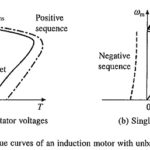
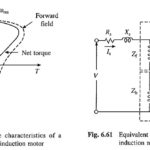
Unbalanced Source Voltages Operations: As Supply voltage may sometimes become unbalanced, it is useful to know the effect of Unbalanced Source Voltages Operations on motor performance. Further, motor terminal voltage may be unbalanced intentionally for speed control or starting as described … (Read More)
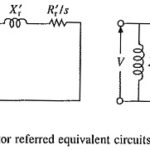
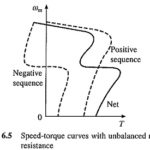
Unbalanced Rotor Impedance Operation: Earlier Unbalanced Rotor Impedance Operation were employed for starting and speed control. They are not in use any more. However, a loose contact in the rotor circuit can cause unbalance in the rotor resistance. It is therefore … (Read More)
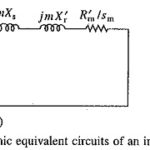
Harmonic Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor: When fed from an inverter or cycloconverter, the motor terminal voltage is non-sinusoidal but it has half-wave symmetry. A non-sinusoidal waveform can be resolved into fundamental and harmonic components using Fourier analysis. Because of half-wave … (Read More)
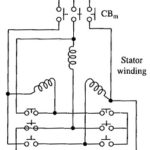
Starting of Induction Motor Drives: Starting of Induction Motor Drives arrangement is chosen based on the load requirements and nature of supply (weak or stiff). It may be required to have following features: Motor should develop enough starting torque to overcome friction, … (Read More)
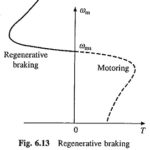
Braking of Induction Motor Drive: Following methods are employed for Braking of Induction Motor Drive: Regenerative braking Plugging or reverse voltage braking Dynamic (or rheostatic) braking further categorised as: ac dynamic braking self-excited braking using capacitors dc dynamic braking zero sequence braking Regenerative Braking: The power input to an induction … (Read More)
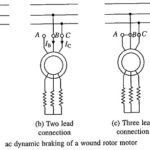
Dynamic Braking of Induction Motor(or Rheostatic Braking): (a) AC Dynamic Braking – AC Dynamic Braking of Induction Motor is obtained when the motor is run on a single phase supply by disconnecting one phase from the source and either leaving it … (Read More)
Transient Analysis of Induction Motor: Usefulness of analysis of transient operating conditions of a drive, e.g. starting, braking, load changing, speed changing, etc. is already explained. A rigorous analysis of transient operation of an induction motor drive, can be done only … (Read More)
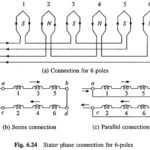
Pole Changing of Induction Motor: For a given frequency, the synchronous speed is inversely proportional to the number of poles. Synchronous speed, and therefore, motor speed can be changed by changing the number of poles. … (Read More)
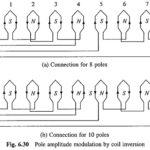
Pole Amplitude Modulation Induction Motor: Pole changing method as already discussed allows a change of speed by a factor 2. In some applications, speed change is required only by a small amount, e.g. some fan and pump drives require speed reduction … (Read More)
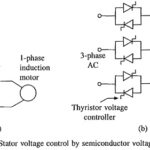
Stator Voltage Control of Induction Motor: By reducing Stator Voltage Control of Induction Motor, speed of a high-slip induction motor can be reduced by an amount which is sufficient for the speed control of some fan and pump drives (Fig. 6.31). … (Read More)
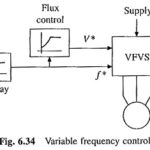
Variable Frequency Control of Induction Motor Drive: Synchronous speed, therefore, the motor speed can be controlled by varying supply frequency. Voltage induced in stator is proportional to the product of supply frequency and … (Read More)
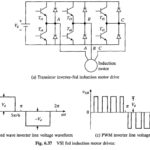
Voltage Source Inverter Control of Induction Motor: Variable frequency and variable voltage supply for induction motor control can be obtained either from a voltage sourve inverter (VSI) or a cycloconverter. Voltage Source Inverter Control of Induction Motor are described here and … (Read More)
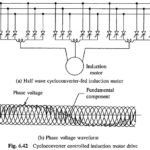
Cycloconverter Control of Induction Motor: Cycloconverter Control of Induction Motor allows variable frequency and variable voltage supply to be obtained from a fixed voltage and frequency ac supply. A half-wave Cycloconverter Control of Induction Motor is shown in Fig. 6.42 along with … (Read More)
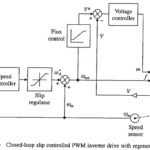
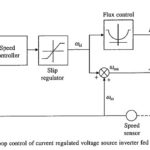
Closed Loop Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives: A Closed Loop Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives is shown in Fig. 6.43. It employs inner slip-speed loop with a slip limiter and outer speed loop. Since for a given current, slip … (Read More)
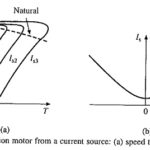
Variable Frequency Control From Current Source: Control of induction motor employing variable frequency voltage sources was considered in previous section. This section considers motor control by Variable Frequency Control From Current Source (VFCS). An equivalent circuit for motor fed from a … (Read More)
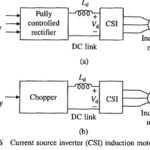
Current Source Inverter Control of Induction Motor: A thyristor Current Source Inverter Control of Induction Motor (CSI) is shown in Fig. 6.45. Diodes D1-D6 and capacitors C1-C6 provide commutation of thyristors T1-T6, which are fired with a phase difference of 60° in … (Read More)
Current Regulated Voltage Source Inverter: Current Regulated Voltage Source Inverter operates with current controlled PWM. In current controlled pulse-width modulation, machine phase current is made to follow a sinusoidal reference current within a hysteresis band. Fig. 6.48(a) shows a sinusoidal reference … (Read More)
Eddy Current Drives: Eddy Current Drives consists of an eddy current clutch placed between an induction motor running at a fixed speed and the variable speed load. Speed is controlled by controlling dc excitation to magnetic circuit of the clutch. Since … (Read More)
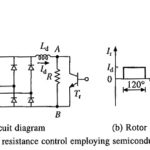
Rotor Resistance Control of Induction Motor: Speed-torque curves for Rotor Resistance Control of Induction Motor are given in Fig. 6.50. While maximum torque is independent of rotor resistance, speed at which the maximum torque is produced changes with rotor resistance. For … (Read More)
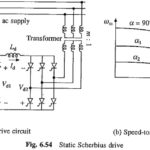
Slip Power Recovery Scheme used in Induction Motor: Figure 6.53 shows an equivalent circuit of a wound-rotor induction motor with voltage Vr injected into its rotor, assuming stator-to-rotor turns ratio unity. When … (Read More)
Variable Speed Constant Frequency Generator: Variable Speed Constant Frequency Generator (VSCF) involves generation of electrical power at fixed frequency and fixed voltage from a variable speed prime mover coupled to the generator shaft. Wind generator is one such example. Speed of … (Read More)
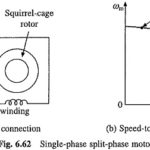
Single Phase Induction Motors Working Principle: Single Phase Induction Motors Working Principle are inferior in performance and lager in weight and volume compared to three-phase motors of the same rating. However, they are simple, robust, reliable and less expensive for small … (Read More)
Single Phase Induction Motor Types: As far as normal running is concerned, a single winding is sufficient. But all motors must be self start. The auxiliary winding is provided to produce finite torque at standstill … (Read More)
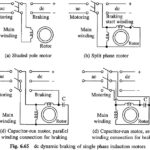
Braking of Single Phase Induction Motor: These motors can be braked by dc dynamic and plugging. The Braking of Single Phase Induction Motor are DC Dynamic Braking: It is commonly used for braking of single phase induction motors. With the help of a double … (Read More)
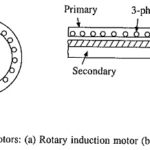
Working Principle of Linear Induction Motor: While the conventional induction motor gives rotary motion, a Working Principle of Linear Induction Motor provides translational or linear motion. Hence it is termed linear induction motor. To understand the principle of operation let us examine … (Read More)