Integrating Sphere in illumination – Construction and Working Principle:
It is a piece of apparatus which is now commonly employed for measurement of mean spherical candle power. In this method the sphere is used to measure the total flux radiated by the lamp, which when divided by 4π gives the mscp. Since in this integrating sphere method the flux radiated in all directions is taken into account, this method is better than that described in which it was assumed that the candle power distribution is same in all vertical planes, an assumption which may not always be justifiable.
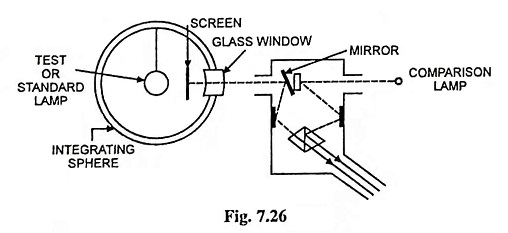
The integrating sphere consists of a hollow sphere whose diameter is large compared to the lamp to be tested having a smooth inner surface with a uniform coating of white paint. If the lamp is hung inside the sphere, the light is so diffused that an uniform illumination is produced over the whole surface. A small window of translucent glass provided at one side of the sphere is illuminated by reflected light from the inner surface of the sphere. The small screen is inserted in between the lamp and window in order to prevent the light from the lamp reaching the window directly.
The measurement of mscp is done as follows :
The lamp, whose mscp is to be determined, is placed at the centre of sphere and brightness of window is measured with the help of some form of illuminometer. The test lamp is replaced by a standard lamp whose mscp is known and brightness of the window is again measured. Since the mscp of the two lamps are proportional to the respective brightness of the window, therefore, the mscp of the lamp under test can be determined by knowing the mscp of standard lamp and brightness of window in the two cases.
A Lummer Brodhun photometer head can also be employed for the measurement of brightness of window with some modifications. A small mirror is placed along with the screen, as shown in Fig. 7.26 in order to reflect the light from the window of the sphere into compound prism of the photometer and balance is obtained using a lamp on the other side of the photometer. Balance is obtained by moving the comparison lamp first with the standard or substandard lamp in the sphere, and then with the lamp test inside the sphere. The squares of the corresponding distance of the comparison lamp from the photometer head is inversely proportional to the mscp of lamps.