Microprocessors and Control for Electric Drives Articles:
Introduction to Microprocessors and Control of Electric Drives: Conventionally, control of thyristor converter fed electrical drives (both dc and ac) is performed using analog discrete components. In the drive control, conventional speed … (Read More)
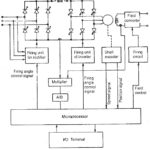
Hardware Systems Versus Microprocessor Control: The Hardware Systems Versus Microprocessor Control control of electric drives offers the following advantages when compared to the dedicated hardware control. As has already been discussed, the use of microprocessors reduces the complexity of the system. The … (Read More)
Applications and Functions of Microprocessors in Electric Drives: With the remarkable progress in the area of microelectronics, reliable and powerful microprocessors have come to be more widely used in the control of electrical drives. A few of the Applications and Functions … (Read More)
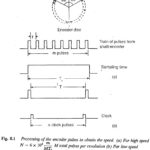
Speed Detector: One important factor in the closed loop control of variable speed drives employing solid state converters is the Speed Detector. In the dedicated hardware control using analog components, the speed sensing is accomplished by means of tachogenerator. For control … (Read More)
Gate Firing Converters: The firing pulse control unit constitutes the heart of any thyristor power converter. The Gate Firing Converters required by the thyristors are often derived from the digital pulses using a simple buffer unit. Analog firing controllers are used … (Read More)
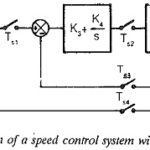
Feedback Control in Drive System: A closed loop control of a variable speed drive system employing thyristor power converters is normally a discrete time system when a microprocessor is implemented for control purposes The system … (Read More)
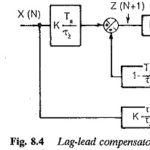
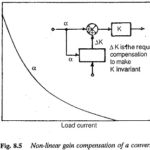
Function Generation and Linearisation: An important aspect of the closed loop control system is the use of Function Generation and Linearisation, e.g. in the control of induction motors there exists a definite nonlinear relationship between the stator current and slip frequency … (Read More)
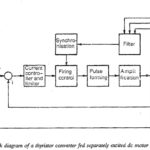
Control of DC Drives Using Microprocessors: The dc motors fed from thyristor converters for variable speeds are being extensively used in general industrial applications. A dual converter, which is a combination of two antiparallel connected three phase/single phase bridge converters, provides … (Read More)
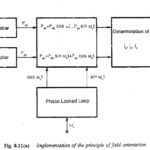
Field Oriented Control of Three Phase Induction Motor: The stator current of an induction motor has the functions of producing the required air gap flux (magnetisation) as well as developing the required torque to drive the load. An Field Oriented Control … (Read More)
Microprocessor Control of Synchronous Motor Drives: Variable speed drives employing Microprocessor Control of Synchronous Motor Drives are becoming very popular in industrial applications. They are an immediate solution for high power reversible drives and are becoming competitors to dc and induction … (Read More)
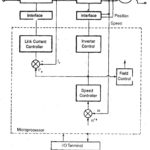
Microprocessor Control of a Current source Inverter Fed Synchronous Motor: A drive system employing a Current source Inverter Fed Synchronous Motor has the following features: A four quadrant drive can be accomplished very easily. A self control, which synchronises the gating pulses of … (Read More)
Inverter Control using Terminal Voltage Sensing: The Inverter Control using Terminal Voltage Sensing of the synchronous motor is obtained using the triggering pulses to the inverter which are synchronized with the rotor position. These signals are obtained by processing the phase … (Read More)
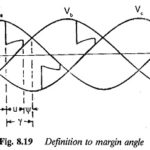
Margin Angle Control of Synchronous Motors: The commutation Margin Angle Control of Synchronous Motors is defined as the angle measured from the end of commutation to the crossing of the phase voltage which was under commutation (natural firing instant). For satisfactory … (Read More)