Motorola 68000 Articles:
Motorola 68000 Features: The Motorola 68000 microprocessor is Motorola’s first 16-bit microprocessor. The 68000 is not program compatible with Motorola’s family of 8-bit microprocessors. For the designing of instruction set the Motorola has given more trace on its powerfulness and simplicity … (Read More)
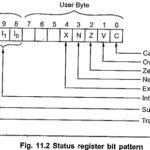
Register Architecture of 68000 Microprocessor: Fig. 11.1 illustrate the Register Architecture of 68000 Microprocessor. Data Registers: The data registers can be used to handle (8-bit) bytes, (16-bit) words, or 32-bit long words. When a data register is used as a source or destination … (Read More)
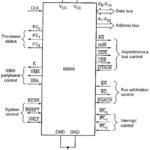
Motorola 68000 Pins and Signals: Fig. 11.3 illustrates the Motorola 68000 Pins and Signals. Data Transfer Control and Address Lines: D0-D15 is the bi-directional 16-bit data bus. A1-A23 is the output 24-bit address bus. The UDS (Upper Data Strobe) and LDS (Lower Data Strobe) … (Read More)
68000 Addressing Modes: 68000 utilizes 14 different 68000 Addressing Modes which can be grouped into 6 basic types. These are 1.Direct Register Addressing a)Data Register Direct b)Address Register Direct 2.Direct Memory Addressing a)Absolute short b)Absolute long. 3.Indirect Memory Addressing a)Register Indirect b)Post-increment Register Indirect c)Pre-decrement Register Indirect d)Register Indirect with Displacement e)Register Indirect … (Read More)
Motorola 68000 Instruction Set: There are actually 56 basic instructions provided in the Motorola 68000 Instruction Set. With 14 addressing modes, 56 instructions, and 5 data types, the 68000 includes more than 1000 opcodes. The basic format of all the instructions … (Read More)
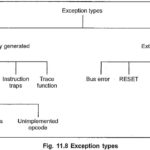
Exceptions Types of Motorola 68000: Exception means an interrupt processing. Like 8086, Exceptions Types of Motorola 68000 also uses a jump vector table to transfer program control to the appropriate handler program, whenever an exception occurs. Operating Modes of 68000: Exceptions Types … (Read More)
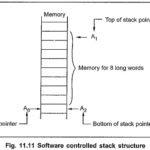
68000 Stack and Queue: 68000 supports stack and queue data structures with the address register indirect position direct and predecrement addressing modes. A stack operates on the principle of Last In First Out (LIFO) and, queue … (Read More)