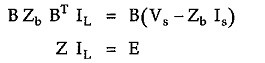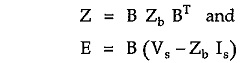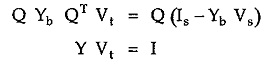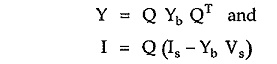Network Equilibrium Equation in Matrix Form:
In earlier section we have studied how to obtain equilibrium equations for a network which are based on loop analysis and node analysis. We can represent the same Network Equilibrium Equation in Matrix Form which simplifies the task of analysis of a large scale network.
Loop or Mesh or KVL Equilibrium Equations:
The KVL equilibrium equations based on loop or mesh analysis are given by
where
The quantities involved in above equations are as follows.
B is the f circuit or tie-set matrix of order (b – n+1) x b,
Zb is the branch impedance matrix of order b x b,
IL is the column matrix of loop currents of order (b – n + 1) x 1
Vs is the column matrix of voltage sources of order b x 1.
Is is column matrix of source currents of order b x 1
Z is coefficient matrix also known as loop impedance matrix of order (b – n +1) x (b – n +1)
E is the column matrix of order (b – n +1) x 1 which represents voltages in loop.
The matrix equation ZIL = E represents a set of (b – n + 1) independent loop equations for a network with n nodes and b branches.
Node or KCL Equilibrium Equation:
The KCL equilibrium equations based on nodal analysis are given by
where
The quantities involved in above equations are as follows.
Q is the f-cutset matrix of order (n -1) x b
Yb is branch admittance matrix of order b x b
Vt is column matrix of tree branch voltages of order (n -1) x 1
Is is the column matrix of branch input current sources of order b x 1
Vs is column matrix of branch input voltage sources
Y is node admittance matrix of order (n -1) x (n -1)
I is the column matrix of order (n -1) x 1 which represents algebraic sum of current sources.