Nuclear Power Plant Articles:
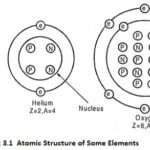
Basics of Nuclear Engineering: Basics of Nuclear Engineering – A matter is composed of atoms. An atom consists of a positive charged nucleus surrounded by a number of negatively charged electrons. The atomic structures of hydrogen, Helium and oxygen are shown … (Read More)
What is Radioactivity? – Definition and Types: The phenomenon of spontaneous emission of powerful radiation exhibited by heavy elements is called radioactivity. It is an irreversible self-disintegrating activity as the elements breaks itself up (fission reaction). The elements that exhibit this … (Read More)
Nuclear Reaction Equation: The Nuclear Reaction Equation are connected with the resettlement of protons and neutrons within the atom. The equations are similar to chemical reactions. The change in the mass of the particle represents the release of energy, that is … (Read More)
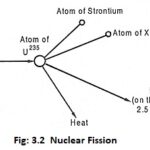
Nuclear Fission and Nuclear chain reaction: Uranium exists in different isotopes of U238, U234 , and U235. Out of these, U235 is the most unstable. When unstable heavy nucleus is bombarded with high energy neutrons, it splits up roughly into two equal fragments … (Read More)
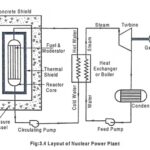
Layout of Nuclear Power Plant: The layout of nuclear power plant is shown in Fig.3.4. The main components of nuclear power plant are 1. Nuclear reactor, 2. Steam generator, 3. Turbine, 4. Coolant pump & feed pump, and 5. Generator. 1. Nuclear reactor: It … (Read More)
Site Selection for Nuclear Power Plant: Assessment of public safety results in greater concern for site selection for a Nuclear power plant. All the natural factors are taken into account like transport of radioactive material to the public during normal operating … (Read More)
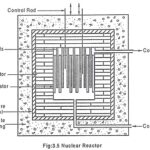
Nuclear Reactor – Definition and its Components: Nuclear reactor is an apparatus which is used to extract the heat produced by the nuclear fission chain reaction. In other words, a nuclear reactor is a controlled chain-reacting system supplying nuclear energy. Mechanism of … (Read More)
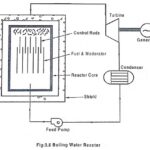
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) – Advantages and Disadvantages: In this Boiling Water reactor, enriched Uranium is used as fuel. Enriched uranium contains more fissionable isotope U235. Water is used as coolant, moderator and reflector like in PWR except the steam is … (Read More)
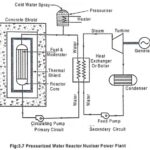
Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) – Working Principle: Pressurized Water Reactor uses enriched U as fuel. In this reactor, water is used as coolant and moderator. The water passes through the reactor core and becomes hot water. The hot water flows to … (Read More)
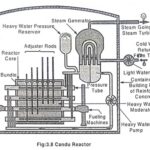
Canada Deuterium Uranium Reactor (CANDU): It is a Canadian invented pressurized heavy water reactor which uses 99.8 percent of Deuterium oxide D2O (Heavy water) as moderator and coolant. The reactor uses 0.7% U235 (natural uranium) as its fuel. The Canada Deuterium … (Read More)
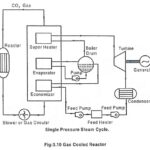
Gas Cooled Reactor Working Process: Gas Cooled Reactor Working Process – This type of reactor is cooled by the gas. The heat carried by the gas from the reactor is either used for generating steam in the secondary circuit like PWR … (Read More)
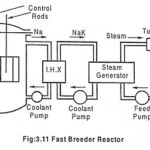
Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) – Definition and Working Principle: Breeding – The process of producing fissionable material from a fertile material such as Uranium 238 (U238) and thorium 232 (Th232) by neutron absorption is known as breeding. The fast breeder reactor system … (Read More)
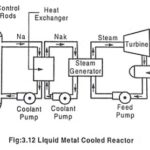
Liquid Metal Cooled Reactor (LMCR) – Working, Advantages & Disadvantages: A liquid metal cooled reactor (LMCR) is an advanced type of nuclear reactor that uses a liquid metal as the primary coolant. The use of liquid metal has many advantages because … (Read More)