Optoelectronics Articles:
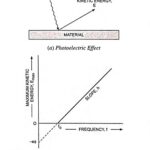
What is Photoelectric Effect? When monochromatic light is incident on a clean surface of a material, then under certain conditions, electrons, also called photoelectrons, are emitted from the surface. The electrons in the metal absorb energy from the light, and some … (Read More)
What is Wave Particle Duality? Since waves exhibit particle-like behavior, then the particles also should exhibit wave—like properties. This theory (de Broglie) is based on the existence of a wave particle duality principle. The momentum of a photon is given as where … (Read More)
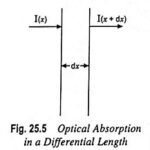
Optical Absorption in Electronics: As discussed in Art. 25.3, light waves can be treated as particles, which are referred to as photons. The energy of a photon is E = hf where h is Plank’s constant and f is the frequency. … (Read More)
Photon Absorption Coefficient: Photon Absorption Coefficient – When light falls on a semiconductor, the photons may be absorbed or they may propagate through the semiconductor depending on the photon energy (E) and the band gap energy EG. Where the photon energy … (Read More)
Luminescence – Definition and Types: When a system absorbs energy in some form or other, it may be partly re-emitted as radiation. This phenomenon is called luminescence. Luminescence may occur in solids (crystals or glasses) as well as in liquids and … (Read More)
Photoconductivity – Definition, Working and its Applications: Photoconductivity – When excess electrons and holes are produced in a semiconductor, there is a corresponding increase in conductivity of a sample as indicated by the following equation Conductivity of semiconductor, The above equation is obtained … (Read More)
Photodetectors – Definition and Applications: Photodetectors are the semiconductor devices that can detect optical signals through electronic processes. The extension of coherent and incoherent light sources into the far-infrared region on one hand and the ultraviolet (UV) region on the other … (Read More)
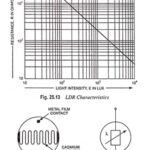
Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs) – Definition, Construction, Workings and Applications: Light dependent resistors (LDRs) are made from cadmium sulphide containing no or very few free electrons when not illuminated. Its resistance is then quite high. When it absorbs light, electrons are … (Read More)
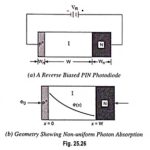
Pin Photodiode – Definition, Working and Applications: The PIN photodiode is one of the most common photodetectors, since the depletion-region thickness (intrinsic layer) can be tailored to optimize the quantum efficiency and the frequency response. The Pin Photodiode is depicted in … (Read More)
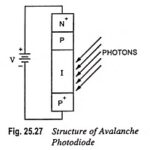
Avalanche Photodiode – Definition, Basic Structure and Workings: The avalanche photodiode is similar to the P-N or PIN photodiode except that it is operated at high reverse-bias voltages so that impact ionization occurs, EHPs are created in the space charge region … (Read More)
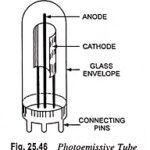
Photoemissive cells or Tubes – Working Principle and Types: These Photoemissive cells or Tubes devices are basically of two types namely vacuum type and gas filled type. 1. Vacuum Type Photocell (or Phototube): This device essentially consists of a thin metal curved sheet … (Read More)
IR Emitters or Infrared-emitting diodes: IR Emitters or Infrared-emitting diodes are solid-state gallium arsenide devices that emit a beam of radiant flux when forward biased. Fig. 25.53 depicts the basic construction of the device. When the junction is forward biased, electrons … (Read More)
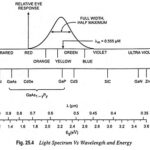
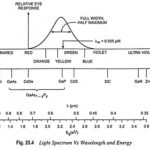
Light Emitting Materials: Since the eye is only sensitive to light of energy hf ≥ 1.8 eV (~ 0.7 μm), semiconductors of interest must have energy band gaps larger than this limit. The band gaps of different binary compound Light Emitting Materials … (Read More)
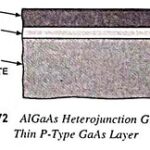
Heterojunction Lasers – Definition, Construction, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications: The device described in previous section was the first type employed in the early development of semiconductor lasers. It is known as an homojunction laser because it contains only one junction … (Read More)
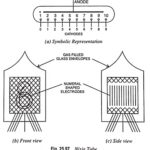
Cold Cathode Display or Nixie Tube – Operation and Characteristics: These are the most well known type of alphanumeric displays. They operate on the basis of emission of light in a cold cathode gas filled tube under breakdown condition. These are … (Read More)
Visual Display Units (VDUs): Large arrays of characters can be built up using alphanumeric devices, already discussed, but the number of connections and the complexity of the drive-logic circuitry increase significantly, although large-scale integrated (LSI) circuits can be employed for this … (Read More)