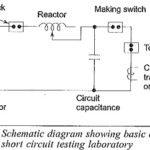
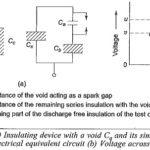
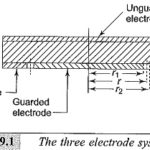
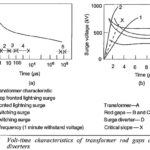
High Voltage Test on Circuit Breaker and Isolators
High Voltage Test on Circuit Breaker and Isolators: High Voltage Test on Circuit Breaker and Isolators is covered, giving common characteristics for both. While these characteristics are directly relevant to…