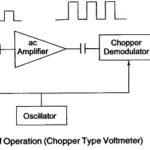
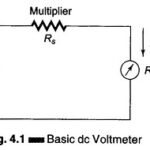
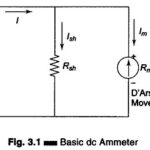
Introduction to Oscilloscopes
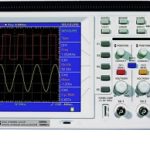
Introduction to Oscilloscopes: Introduction to Oscilloscopes - The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope is probably the most versatile tool for the development of electronic circuits and systems. The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope allows…