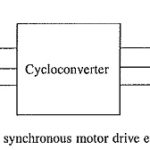
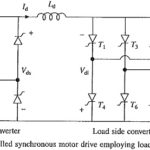
Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive Employing a Cycloconverter
Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive Employing a Cycloconverter: Self Controlled Synchronous Motor Drive Employing a Cycloconverter as shown in Fig. 7.13. Firing pulses are generated either by comparison of the…