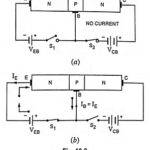
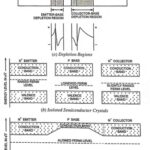
Transistor Lead Identification and Testing
Transistor Lead Identification and Testing: Transistor Lead Identification and Testing - After the transistor has been manufactured, as already discussed, leads of, typically, gold, aluminium, or nickel are then attached…