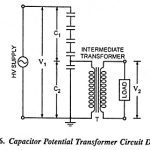
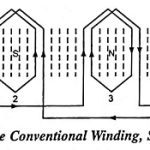
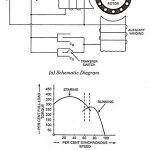
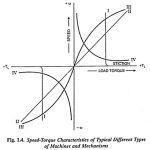
Instrument Transformers – Definition, Types and Errors
Instrument Transformers - Definition, Types and Errors: AC type protective relays are actuated by current and voltage supplied by current and potential (or voltage) transformers, known as instrument transformers. The…