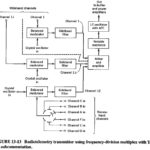
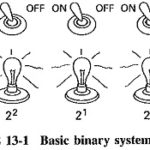
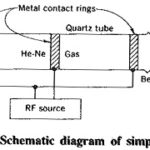
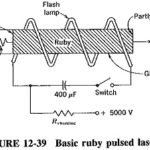
Telemetry in Electronic Communications
Telemetry in Electronic Communications: Telemetry in Electronic Communications consists of performing measurements on distant objects. Although hydraulic or wire circuits may be used for this purpose, this section will deal…