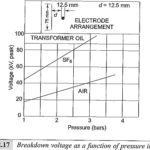
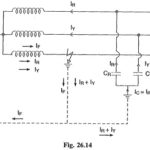
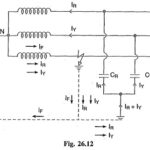
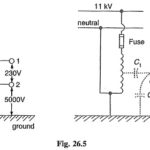
Characteristics of Liquid Dielectrics
Characteristics of Liquid Dielectrics: Essential Characteristics of Liquid Dielectrics should possess good dielectric properties, excellent heat transfer characteristics and must be chemically stable under the range of conditions under which the…