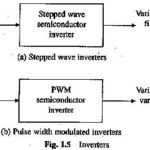
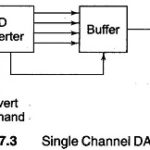
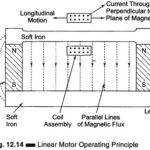
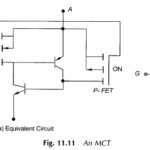
Electronic Devices and Circuits Articles
Electronic Devices and Circuits Articles: This Electronic Devices and Circuits Articles which includes the following topics: Introduction to Semiconductor Materials and Devices Conduction in Solids Conductor Semiconductor and Insulator P…