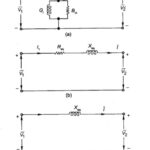
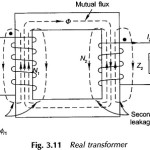
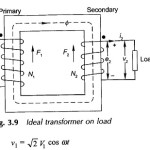
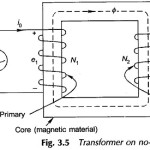
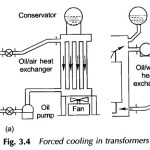
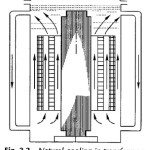
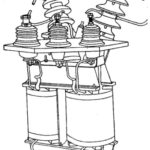
Approximate Equivalent Circuit of Transformer
Approximate Equivalent Circuit of Transformer: Approximate Equivalent Circuit of Transformer - In constant frequency (50 Hz) power transformers, approximate forms of the exact T-circuit equivalent of the transformer are commonly…