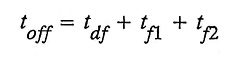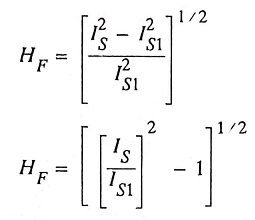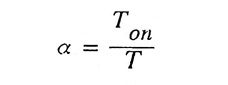Power Electronics Interview Questions and Answers:
Following are the below Power Electronics Interview Questions and Answers, Power Electronics Important Questions and Answers
1. State the conduction to be satisfied for the load commutation in SCR.
Ans. For achieving load commutation of a thyristor, the commutating components L and C are connected in series with R and overall circuit must be underdamped.
2. Define “Turn off time” of SCR.
Ans. Turn off time of SCR composed of three intervals delay time tdf, initial fall time tf1 and final fall time tf2
3. What is meant by line commutated inverter?
Ans. Phase controlled converters when operated in the inverter mode, are called line commutated inverter.
4. What are the advantages of SMPS over factors controlled rectifiers?
Ans.
- Small size and less weight.
- High efficiency.
- Less sensitive to input voltage variations.
5. Give the uses of resonant switching.
Ans. The switching devices are made to turn-ON and turn-OFF at high di/dt. Hence there is increased power loss in these devices. This can be minimized if each switch is turned-ON/OFF when the voltage across it is zero or when the current through it is zero.
6. What is meant by current source inverter?
Ans. In current source inverter the source used in current source, which is obtained by using an inductor in series with the voltage source and the load current does not dependent on the load impedance.
7. Why is the series inverter called so?
Ans. Inverters in which commutating components (L and C) are permanently connected in series with the load, hence called as series inverters.
8. What are the applications of cycle converter?
Ans.
- Speed control of high-power ac drives.
- Induction heating.
- Static Var compensation.
- For converting varibale-speed alternator voltage to constant frequency output voltage for use as power supply in aircraft or shipboards.
9. Why are IGBT becoming popular in their applications to controlled converters?
Ans. IGBT combines it with the advantages of both MOSFET and BJT. So an IGBT has high input impedance like a MOSFET and low on state power loss as in a BJT. IGBT is free from second breakdown problem present in BJT.
10. Define the term pinch off voltage of MOSFET.
Ans. Pinch-off voltage defines as the maximum gate current applied to MOSFET to increase the depletion layer between source and drain, which limits the current flowing into the drain. So the current saturates and the output current remains constant.
11. Under what conditions a single phase fully controlled converter gets operated as an inverter.
Ans. If the firing angle α 90° means the single phase fully controlled bridge rectifier with RL load operates in the inversion mode, the average.value of output voltage is negative maximum. Hence the net power flow is from DC to AC side and sets like inverter.
12. Define total harmonic distortion (THD).
Ans. The harmonic factor (HF) of the input current is defined as
HF is a measure of distortion of a waveform and is also known as total harmonic distortion (THD).
13. Define the term duty cycle in dc-dc converters.
Ans. Duty cycle is defined as a ratio of an time of the chopper to the total time of the chopper.
14. What is a DC chopper?
Ans. A DC chopper is a high speed static switch used to obtain variable dc voltage from a constant dc voltage.
15. Define the term inverter gain.
Ans. The ratio of RHS voltage of line to the supply voltage is known as invertor gain.
16. What is cycloconverter?
Ans. Cycloconverter converts input power at one frequency to output power at a different frequency with one stage conversion.
17. What is meant by integral cycle control?
Ans. The thyristors are employed as switches to connect the load circuit to the source for a flew cycles of the same voltage and disconnected it for another few cycles. This method of operation is called integral cycle control.
18. What are the drawbacks of GTO?
Ans.
- magnitude of latching and holding currents is more in a GTO.
- on state voltage drop and associated loss is more in GTO.
- gate drive circuits losses are more and reverse-voltage blocking capacity is less than its forward-voltage blocking capability.
19. What is latching current of SCR?
Ans. The SCR is conducting in a forward current that is greater than the minimum value called the latching current, the gate signal is our longer required to maintain the devices in its ON = state.
20. Why is power. factor of semi converter better than full converter?
Ans. For supplying given load, the semi-converter receives less reactive power due to free wheeling action when compared with full converter. Therefore, the power factor is better in semi-converter.
21. What is the inversion mode of rectifiers?
Ans. If α > 90°, the voltage at the load terminal is negative, therefore the power flows from dc side to ac side and the converter operates so a line commutated inverter.
22. What is constant frequency control of chopper?
Ans. The on-time TON is varied but chopping frequency f is kept constant. Variation of TON is by means of adjusting the pulse width.
23. What are the advantages of PWM inverters?
Ans.
- The output voltage control with this method can be obtained without any additional components.
- Lower order harmonic can be eliminated or minimized along with its output voltage control.
- Higher order can be filtered easily, the filtering requirements are minimized.
24. Write the principle of operation of cycloconverter.
Ans. A cycloconverter is a frequency changer that converts ac power at one frequency to ac power at different frequency without any intermediate dc link.
ac power at one frequency → Cycloconverter → at different frequency
25. Give any two important applications of AC voltage controllers.
Ans.
- Domestic and industrial heating
- Transformer tap changing
- Lighting control
- Starting of induction motor.
26. What is the limitation of high frequency operation of a power electronic device?
Ans. Limitations of High Frequency Operation:
- Switching losses will be high.
- Switching stress will be high.
- Harmonics in distortions can be increased.
27. What is the use of snubber circuit?
Ans. Use of Snubber Circuit:
- It is used to prevent the derive from dv/dt.
- It provides the path for sudden current rise due to sudden voltage across the circuit.
28. What is displacement factor for two pulse converter?
Ans. It is defined as the cosine of the displacement angle DF = cos α.
29. What is current turn-off time for single phase full converter?
Ans. Circuit turn-off time for single phase full converter is defined as the SCR is reverse biased by the commutation circuit.
30. What are the control strategies for Chopper circuit?
Ans. There are two control strategies for chopper. They are:
- Time ratio control.
- Current limit control.
31. What is the need for resonant converter?
Ans. Need for Resonanct Converter:
- The switches are free from high voltage stress.
- The switches power losses are reduced.
- The electromagnetic interference also reduced.
- The derive thru-Q and turn-off time will not overlap with other.
32. In a CSI, if frequency of output voltage is ‘f’ Hz, what is the frequency of voltage input to CSI?
Ans. The frequency of voltage input will be the same as that of output voltage frequency.
33. What is space vector?
Ans. It is derived from the rotating field of AC machine which is used for modulating the inverter output voltage.
34. What are the types of ac voltage controllers?
Ans. Types of ac Voltage Controllers:
- Single phase ac voltage controllers.
- Three phase ac voltage controllers.
35. What is matrix converter?
Ans. Matrix converter is capable of direct conversion from AC to AC by using bi-directional fully controlled switches.