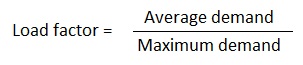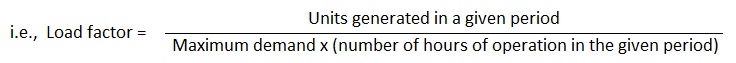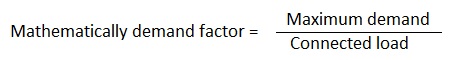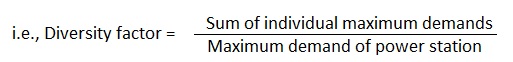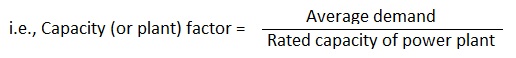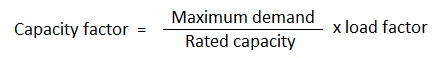Power Plants Economics Interview Questions and Answers:
1. State factors on which generating cost depends.
Ans. The generating cost per unit (kWh) of energy depends upon the cost covering the purchase, installation and erection of equipment, cost of fuel, labour, repair etc.
2. What items constitute the fixed and running charges of generation of electrical energy ?
Ans. The fixed charges include the annual interest and depreciation on the capital cost of generating plant, transmission and distribution network, buildings and other civil works, all types of taxes and insurance charges and salaries of high officials, management and clerical staff and compensation given to the workers.
The running or operating cost includes annual costs of fuel, lubricating oil, water, maintenance and repairs of equipment and salaries of operational and maintenance staff and salaries of supervisory staff engaged in the running of the plant.
3. Why is fixed cost independent of maximum demand and units generated?
Ans. Fixed cost is due to the annual cost of central organisation, interest on the capital cost of land (especially if some land is held for future development) and salaries of high officials.
The annual expenditure on central organization and salaries of high officials is fixed since it has to be met whether the plant has high or low maximum demand or it generates less or more energy (units). Further, the capital investment on the land is fixed and hence the amount of interest is also fixed. As such fixed cost is independent of maximum demand and units generated.
4. What is depreciation reserve?
Ans. The depreciation charge represents the amount which is set aside from income every year so as to produce a sufficient sum at the end of the probable life for replacing the plant and machinery by new ones and the amount so accumulated is called the depreciation reserve.
5. What do you mean by off peak energy utilization?
Ans. Off peak energy utilization means encouraging the consumers to use electricity during off peak hours by giving a special discount. Its benefits are : 1. Improvement of plant capacity factor resulting in reduction of capital cost and better utilization of investment. 2. Reduced requirement for peaking units resulting in lower plant capacity and lower production and maintenance costs of fossil peaking units.
6. How does the load duration curve differ from chronological load curve ?
Ans. The daily variations in load on the power station from time to time—hourly or half hourly can be plotted on a graph taking load on Y-axis and time on X-axis. The curve so obtained is known as chronological load curve. The load duration curve indicates the variation of load, but with the load arranged in descending order of magnitude i.e., the greatest load on the left, lesser loads towards the right hand and the least load at the extreme light.
7. What information’s can be supplied by load curves ?
Ans. The information’s that can be had from load curves are (i) variations of load during different hours of the day (ii) total number of units generated in a day (iii) maximum demand on the power station (iv) average load and (v) load factor.
8. Define energy load curve.
Ans. Energy load curve gives the total number of units generated for the given demand. The ordinate represents the demand in kW or MW and the abscissa represents the units (kWh) generated at or below a given demand (in kW or MW). Such a curve can be obtained from the load duration curve keeping the abscissa corresponding to each ordinate equal to the area of the duration curve up to the value of that ordinate.
Such curves are useful in that with a given number of units (kWh) available, say from a river flow, the load (kW) that could be carried at the base or peak may be easily determined.
9. How does energy load curve differ from mass curve ?
Ans. The curve drawn between demand in kW or MW on Y-axis and units generated (kWh) on X-axis is known as integrated load duration curve or energy load curve while mass curve is plotted with units (kWh) generated as ordinate and time as abscissa.
10. What is load factor ?
Ans. The ratio of average load to the maximum demand during a certain period of time such as a day or a month or a year is called the load factor. Since average load is always less than the maximum demand, load factor is therefore, always less than unity.
Load factor may also defined as the ratio of the number of units actually generated in a given period to the number of units which could have been generated had the load or demand remained at the maximum value throughout this period.
11. Can the load factor of the system be 100% ?
Ans. Since average load is always less than the maximum demand, load factor being the ratio of average load to maximum demand is always less than unity. As such load factor of the system cannot be 100%.
12. Why even if the maximum demand and load factor of the two systems are equal, their load duration curves may not be similar?
Ans. Load factor is the ratio of average load to maximum load. Even if load factor and maximum demands are the same, the load duration curve, which is plotted between the load in MW and time (load arranged in descending order of magnitude) and indicates the total number of units generated for the period considered, may not be same. This is because the maximum demand may not occur simultaneously. Thereby, the area under load duration curves might be same but they might differ in shape.
13. Define demand factor.
Ans. The ratio of actual maximum demand on the system to the total rated load connected to the system is called the demand factor. It is always less than unity.
The idea of a demand factor was introduced due to the fact that all the equipment connected to the system will not be worked at a time in practice and the kW or kVA maximum demand of a group of electricity consuming devices will be always less than the sum of the kW or kVA ratings or capacities of these devices.
The minimum capacity of the generating plant must be such as to meet the maximum demand, the value of demand factor, therefore, determines the capacity and hence cost of the power equipment required to serve a given load.
14. Can demand factor be more than 1?
Ans. Demand factor, defined as the ratio of maximum demand on the system to the total rated load connected to the system, cannot be more than unity because maximum demand on the system can never be more than rated load connected to the system.
15. What is diversity factor?
Ans. The maximum demands of all the consumers supplied from an installation do not occur usually at the same time, maximum demand on the installation is, therefore, always less than the sum of individual maximum demands of all consumers connected to it.
The ratio of sum of the individual maximum demands of all the consumers supplied by it to the maximum demand of the power station is called the diversity factor.
It is always greater than unity.
16. Differentiate between diversity factor and load factor.
Ans. Diversity factor is defined as the ratio of the sum of the individual maximum demands to maximum demand of the group whereas load factor is defined as the ratio of average load to the maximum demand.
17. Discuss why, maximum demand of a group of consumers is always less than the sum of their individual maximum demands?
Ans. The maximum demands of all the consumers supplied from an installation do not occur usually at the same time, maximum demand on the installation is, therefore, always less than the sum of individual maximum demands of all consumers connected to it.
18. What is diversity factor and how does it influence the cost of generation ?
Ans. The ratio of sum of individual maximum demands of all the consumers supplied by it to the maximum demand of the power station is called the diversity factor. It is always greater than unity. Higher the diversity factor better it is. With a given number of consumers the higher the diversity factor of their loads, the smaller will be capacity of the power plant required and consequently the fixed charges due to capital investment will be much reduced.
19. How is diversity helpful in reducing the costs?
Ans. Diversity helps in reducing the costs as the diversity would mean that the maximum demands of all the consumers supplied from an installation would not occur at the same time, this would reduce total maximum demand on the installation. With a given number of consumers the higher the diversity factor of their loads, the smaller will be capacity of the power plant required and consequently the fixed charges due to capital investment will be much reduced.
20. What is capacity factor?
Ans. Every plant has to have a reserve capacity so as to take care of the future expansion and increase in load and, therefore, total installed capacity of the plant is usually greater than that actually required (maximum demand).
Capacity (or plant) factor is defined as the ratio of the average load to the rated capacity of the power plant.
Plant capacity factor may also be defined as the actual energy generated divided by the maximum possible energy that the plant might have generated during a given period.
The capacity factor depicts the extent of the use of the power plant. It is different from load factor and the difference is an indication of the reserve capacity.
21. Discuss why utilization factor of a plant may even be greater than unity?
Ans. Utilization factor is a measure of the utility of the power plant capacity and is defined as the ratio of maximum demand to the rated capacity of the power plant. It is always less than unity because power plant is never operated beyond its rated capacity.
22. Explain various types of reserves in power system.
Ans. Every system must have certain amount of reserve generating capacity to provide for overhaul of generating equipment, forced outage of equipment etc. Various types of reserves are given below.
Operating reserve refers to capacity in service in excess of peak load. It is provided for regulation within the hour to cover minute to minute variations, load forecasting errors, loss of equipment and maintenance of equipment. It consists of spinning and/or non spinning reserve.
- Spinning Reserve : It is the generating capacity connected to the bus and ready to take load. In order to take instantaneous peak loads, the system must have capacity in readiness to serve. For this purpose certain machines are kept running on no load i.e., floating on the system. This is called the spinning reserve of the system.
- Non Spinning Reserve is that operating reserve which is capable of being connected to the bus and loaded within a specified time.
23. What is no spinning reserve?
Ans. Non Spinning Reserve is that operating reserve which is capable of being connected to the bus and loaded within a specified time.
24. What do you understand by (i) base load and (ii) peak load of a power plant?
Ans. The unvarying load, which occurs almost the whole day on the power plant is called the base load whereas the various peak demands of the load over and above the base load of the power plant is called the peak load.
25. Differentiate between base load plants and peak load plants.
Ans. Base load plants run throughout the year and have high load factors. The economic characteristics of base load plants should be such that they supply power at high capital costs but low cost of operation. Hydro and nuclear power plants are usually classified as base load plants. Peak load plants run for a few hours in the year and work at low load factors. The economic characteristics of peak load plants should be such that they supply power at low capital costs, although at high cost of operation. Peak load power plants should be capable of starting quickly and should be inexpensive in starting and shutting down operations.
26. Generally which type of generation is used for base load demand?
Ans. The economic characteristics of base load plants should be such they supply power at high capital cost but low operating cost. Hydro and nuclear power plants are usually used for supplying base load demand.
27. Define load forecasting.
Ans. Prediction of load on the system for future is termed as load forecasting.