Power Semiconductor Devices Articles:
What is Thyristor? – Thyristor Family and its Applications: Thyristor is the general name given to a family of semiconductor devices having four layers with a control mechanism, although this term is most commonly applied to the SCR (silicon controlled rectifier). … (Read More)
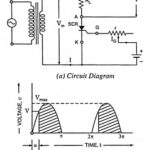
SCR as Half Wave Rectifier Circuit Diagram: SCRs are very useful in ac circuits where they may serve as rectifiers whose output current can be controlled by controlling the gate current. An example of this type of application is the use … (Read More)
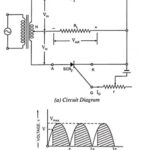
SCR as Full Wave Rectifier Circuit Diagram: For Two SCR as Full Wave Rectifier are connected across the centre taped secondary, as shown in Fig. 26.32 (a). The gates of both SCRs are supplied from two gate control supply circuits. One … (Read More)
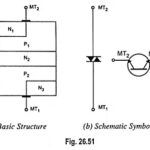
What is DIAC? – Symbol, Construction, Operation and Applications: A diac is an important member of the thyristor family and is usually employed for triggering triacs. A diac is a two electrode bidirectional avalanche diode which can be switched from off-state … (Read More)
Shockley Diode Equation, Symbol, Operation and Applications: The four layer diode, also called the Shockley diode after its inventor Willian Shockley, is essentially a low-current SCR without a gate. It is classified as a diode because it has only two external … (Read More)
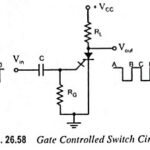
Gate Controlled Switch (GCS) Circuit – Operation and Advantages: As mentioned earlier, low-current drop out is the normal way in which the SCR is turned off. Gate controlled switch is designed for easy opening with a reverse-biased trigger. A GCS is closed … (Read More)
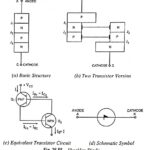
Silicon Controlled Switch (SCS) – Symbol, Operation, Advantages and Application: Silicon controlled switch (SCS), like the SCR, is a unilateral, four layer, three junction P-N-P-N silicon device with four electrodes namely cathode C, cathode gate G1, anode gate G2 and the … (Read More)
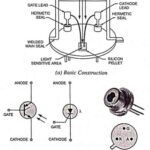
Light Activated SCR (LASCR) – Symbol, Construction and Operation: Light activated SCR is just an ordinary SCR except that it can also be light triggered. Most LASCRs also have a gate terminal for being triggered by an electrical pulse just as … (Read More)
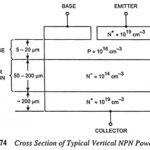
Power BJT – Construction, Operation and its Characteristics: Power transistors are large-area devices. Because of differences in geometry and doping concentrations, their properties tend to vary from those of the small-signal devices. The structure of a vertical NPN power transistor is … (Read More)
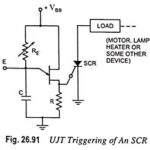
UJT Triggering of SCR Working Principle: UJT Triggering of SCR Working Principle – One common application of the unijunction transistor is the triggering of the other devices such as the SCR, triac etc. The basic elements of such a triggering circuit … (Read More)
UJT Relaxation Oscillator – Circuit Diagram and its Workings: UJT Relaxation Oscillator – The relaxation oscillator shown in Fig. 26.94 (a) consists of UJT and a capacitor C which is charged through resistor RE when interbase voltage VBB is switched on. … (Read More)
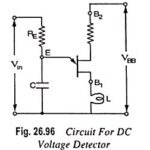
UJT as Over Voltage Detector Circuit Diagram: UJT as Over Voltage Detector Circuit Diagram – A simple dc overvoltage detector circuit is given in Fig. 26.96. It operates on the fact that the device remains switched off as long as the … (Read More)