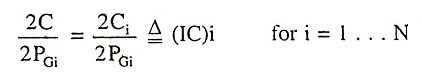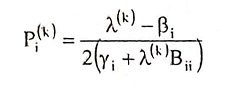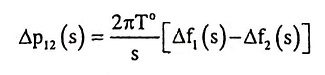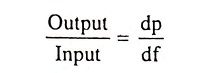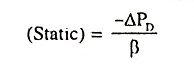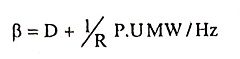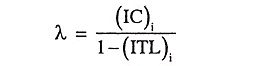Power System Control Interview Questions and Answers:
Following are the below Power System Control Interview Questions and Answers, Power System Control Important Questions and Answers
1. What is the need for voltage regulation in power systems?
Ans. Power sytem has many equipments. All the equipments in power station are designed to operate satisfactorily only when voltage level on the system correspond to their rated values. So the voltage regulation is very important.
2. State whether changes in AVR loop will be reflected in ALFC loop.
Ans. The AVR and ALFC loops are not in the trust sease noninteracting a class coupling does exist and can sometimes be troublesome. There is little if any coupling from the ALFC loop to the AVR loop, but interaction exists in the opposite direction. However the AVR loop is much faster than the ALFC loop and there is therefore a tendency for the AVR dynamics to settle down before they can make themselves felt in the slower load frequency control channel.
3. State the basic role of ALFC.
Ans. The Automatic load Frequency Control (ALFC) loop regulates the megawatt output and Frequency (speed) of the generator. The loop is not a single one as in the case of AVR.
4. What is meant by a control area?
Ans. Most Power Systems normally control their generators in unison. The individual control loops have the same regulation parameters. If also and this is quite important the individual generator turbines tend to have the same response characteristics then it is possible to control ALFC loop represent the whole system which then would be referred to as control area.
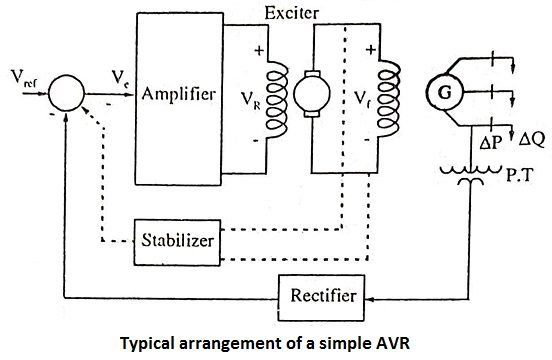
5. List the various components in AVR loop.
Ans. The following are the components of AVR loop
- Exciter
- Transformer
- Amplifier
- Generator
- Comparator
- Rectifier, filter
6. What is a synchronous condenser?
Ans. An overexcited synchronous machine operated either as motor or generator produces reactive power and acts as a shunt capacitor is called as synchronous condensor.
7. List the various controls to ensure secured operation of a power system.
Ans.
- Preventive control
- Emergency controls
These control actions may be initiated from the central energy control center either automatically or by operator intervention. If speed of action is of extreme important the control actions are implemented through local means.
8. List the factors that affects the power system security.
Ans. Security is an operational problem that will change with operational conditions. It depends not only upon the reserve capacity available in a given situation but also upon the contingent probability of disturbances.
9. Explain the term incremental operation cost of a power system.
Ans.
The derivative 2Ci/2PGi are referred to as incremental operating cost of generation. They represent the slope of the cost curve. As the unit for Ci is dollars per hour, the K unit must be dollars per hour per Kilowatt or dollars per kilowatt hour.
10. Give the two major control loops of large generators.
Ans.
The Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) loop controls the magnitude of the terminal voltage V.
The Autoinatic Load Frequency Control (ALFC) loop regulates the Megawatt output and frequency (Speed) of the generator.
So AVR, ALFC are the two major control loops of large generators.
11. What is the basic principle in pool operation?
Ans. A basic guiding principle in pool operation must be that each area in normal steady state absorbs its own load. Pool operation can benefit the individual members in terms of margin need, peaking capacity and better use of load and generation diversity.
12. Specify the disadvantages of ALFC loop.
Ans. The ALFC loop will maintain control only during normal (small and slow) changes in load and frequency. It is typically unable to provide adequate control during emergency situation, when large megawatt inbalances occur. Then more drastic emergency controls must be applied.
13. Draw a typical arrangement of a simple AVR.
Ans.
14. Give the two kinds of capacitors used in shunt compensator.
Ans.
- Static VAR compensator
- Static synchronous compensator (STATCOM)
15. What is DAC?
Ans. DAC is a low version of SCADA applicable in distribution system (including loads) which of course draws power from the transmission/sub.transmission levels obviously then there is no clear cut demacation between DAC and SCADA.
16. Give some of the inputs used in DAS.
Ans.
Analog inputs:
- Pressure, flows, electrical parameters etc
- Analog input of 0-10 V DC
- Thermocouple
- RTD input
Digital inputs:
- Contract outputs
- Valve position, pressure and limit switches
17. What is meant by incremental cost curve?
Ans. The incremental fuel cost curve is a measure of how costly it will be to product the next increment of power. The total operating cost includes the fuel cost and the cost of labour, supplies and maintenance. These costs are assumed to be a fixed percentage of the fuel cost and are generally included in the incremental fuel cost curve.
18. Write the coordination equation taking losses into account.
Ans.
19. What is the necessity of frequency regulation in power systems?
Ans. The necessity for frequency regulation arises out of the following reasons.
- Most of A.C motor runs at a speed that are directly related to the frequency.
- The generator of steam driven turbines are designed to operate at a very precise speed.
- Constant turbine speed is an important requirement. The velocity of expanding steam is beyond control and turbine efficiency requires a perfect match in speed.
- Electrically operated clocks are used. They are all driven by synchronous motor and accuracy of these clocks is a function not only of a frequency error but actually of the integral of this error.
20. State about real-time control of power systems.
Ans. Generally more peak load demand must be met by older plant. Therefore monitoring and control systems must be fast enough to protect generation equipments against overloads, false and dangerous operating conditions. Conventional electrical instruments can handle the situation if the information received is one at a time. But when multiple information is available, a fast data processing equipment is required which is obtained from a computer based terminal unit.
The benefits obtained from a computerized operation and control of a plant are (a) Increased plan safety (b) more equipment life (c) Increased plant availability (d) Higher plant efficiency (e) minimum operating errors.
21. Write the tie-line power deviation equation in terms of frequency.
Ans.
22. Name the methods of voltage control in network.
Ans.
The following are the methods of voltage control
- By excitation control
- By static series capacitors
- By static shunt capacitors
- By static shunt reactors
- By synchronous condenser
Other methods of voltage control
- Tap changing transformer
- Regulating transformer
- Booster transformer
- Static VAR compensators
23. Specify the location and nature of tap changing transformers.
Ans. A tap changer is provided on a transformer for maintaining, specified out going voltage where the incoming voltage is subjected to voltage variations. The tap changer is mounted in on the transformer tank. It comprises a motor driven mechanism and associated control circuit for starting and stopping the motor. The motor can be run in the direction for a rise tap changer or in the reverse direction for a lower tap changer.
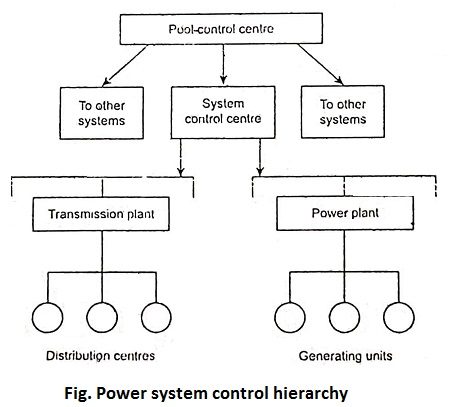
24. Denote the hierarchical levels used in EMS.
Ans.
25. Mention four types of SCADA systems and its application area.
Ans.
- Type 1: Small distribution system small Hydrostation HVDC link
- Type 2: Medium sized power system power stations. HVDC links distribution system
- Type 3: Regional control centre
- Type 4: National & Regional control centres
26. Define incremental efficiency.
Ans. Incremental efficiency is defined as the reciprocal of incremental fuel rate or incremental production cost and is given by
27. List the various constraints in the modern power systems.
Ans. Power system operations have the responsibility to ensure that adequate power is delivered to the load reliably and economically in order to ensure adequate delivery of power demand. The electric energy system should be capable of being operated at the desired operating point by automatic maintenance of nominal frequency voltage profile and load flow configuration. The real and reactive power should be capable of being controlled automatically. The generated electrical power unit must satisfy the load demand.
28. What happens to frequency if the load on the generator increases?
Ans. When the load on the generator increases the frequency decreases.
29. Define area control error.
Ans. If the frequency drops by 1Hz (Δf = -1) then the integrator calls for an increase in power with the “call” increasing at the initial rate of Kf pu MW/s. Note the negative polarity of integral controller. This polarity must be chosen so as to cause a positive frequency error to give rise to a negative or decrease its command. The signal fed to the integrator is referred to area control error (ACE).
30. What is meant by AFRC?
Ans. In the analysis of load .frequency control of single control area under the classification of uncontrolled case we get an expression Δf
where
β is called area frequency response characteristics
31. What is SVC? State its advantages.
Ans. SVC is nothing but static VAR compensator
SVC can maintain specific voltage profile and can limit the voltage and frequency derivations under disturbances. Transient stability can be improved and system transmission capacity can be increased both under operating and fault conditions.
32. Where are synchronous condensers installed?
Ans. Synchronous condensers are located at
- Generating stations
- Transformer stations
- Feeders
33. What do you understand by SCADA system?
Ans. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition sygtem allows a few operator to monitor the generators and HV Transmission system.
34. Write the co-ordination equation taking the effect of losses.
Ans.
Where
- IC = incremental cost
- ITL = incremental transmission loss
35. What is the criteria that should be satisfied for economic loading of generating stations?
Ans.
- The incremental cost of production of a plant is always positive, the incremental transmission losses can be both positive or negative.
- The individual generators will operate at different incremental costs of production.
- The generator with the highest positive incremental transmission loss will operate at the lowest incremental cost of production.
36. What is the function of load control centre?
Ans. Load control centre performs the following controls:
- Load Forecasting
- Economic Dispatch
- System planning
- Load frequency control